Modeling the effect of alcohol on smoking lapse behavior
- PMID: 17013640
- PMCID: PMC2862311
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-006-0551-8
Modeling the effect of alcohol on smoking lapse behavior
Abstract
Objective: The primary aim of this project was to examine the role of alcohol use in smoking lapse behavior, as alcohol consumption is a known risk factor for poor smoking cessation outcomes.
Materials and methods: We have developed a novel human laboratory model to examine two primary aspects of alcohol-mediated tobacco relapse: (1) Does alcohol facilitate the initiation of the first cigarette? (2) Once the first cigarette is initiated, does alcohol facilitate subsequent smoking? Using a within-subject design, 16 daily smokers who were also heavy social drinkers received a priming drink (0.03 g/dl or taste-masked placebo) and then had the option of initiating a tobacco self-administration session or delaying initiation by 5-min increments for up to 50 min in exchange for monetary reinforcement. Subsequently, the tobacco self-administration session consisted of a 1-h period in which subjects could choose to smoke their preferred brand of cigarettes using a smoking topography system or receive monetary reinforcement for cigarettes not smoked. Alcohol craving, tobacco craving, subjective reactivity to alcohol, and nicotine withdrawal were assessed as secondary outcomes.
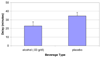
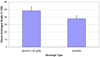
Results: Results demonstrated that after consuming the alcohol beverage, subjects were less able to resist the first cigarette and initiated their smoking sessions sooner, and smoked more cigarettes compared to the placebo beverage. These findings have implications for smoking cessation in alcohol drinkers and model development to assess smoking lapse behavior.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotine and food deprivation decrease the ability to resist smoking.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Sep;212(1):25-32. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1902-z. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20585761 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Stress decreases the ability to resist smoking and potentiates smoking intensity and reward.J Psychopharmacol. 2011 Apr;25(4):490-502. doi: 10.1177/0269881110376694. Epub 2010 Sep 3. J Psychopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20817750 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alcohol-induced increases in smoking behavior for nicotinized and denicotinized cigarettes in men and women.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Nov;207(1):107-17. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1638-9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19756530 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Developing human laboratory models of smoking lapse behavior for medication screening.Addict Biol. 2009 Jan;14(1):99-107. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00135.x. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Addict Biol. 2009. PMID: 18855800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smoking behaviour and compensation: a review of the literature.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1999 Jul;145(1):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s002130051027. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1999. PMID: 10445368 Review.
Cited by
-
Drinking patterns of older adults with chronic medical conditions.J Gen Intern Med. 2013 Oct;28(10):1326-32. doi: 10.1007/s11606-013-2409-1. Epub 2013 Apr 23. J Gen Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23609178 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of alcohol and tobacco/nicotine interactions in the human laboratory.Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017 Mar;43(2):186-196. doi: 10.1080/00952990.2016.1189927. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017. PMID: 27439453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral economic analysis of cue-elicited craving for tobacco: a virtual reality study.Nicotine Tob Res. 2013 Aug;15(8):1409-16. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nts341. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Nicotine Tob Res. 2013. PMID: 23322768 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine interactions with low-dose alcohol: pharmacological influences on smoking and drinking motivation.J Abnorm Psychol. 2013 Nov;122(4):1154-65. doi: 10.1037/a0034538. J Abnorm Psychol. 2013. PMID: 24364618 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Situational fears: Association with negative affect-related smoking cognition among treatment seeking smokers.Addict Behav. 2018 Oct;85:158-163. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Jun 9. Addict Behav. 2018. PMID: 29907345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babor TF, de la Fuente JR, Saunders J, Grant M. AUDIT: The alcohol use disorders identification test: Guidelines for use in primary health care. Genva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1992.
-
- Baer JS, Lichenstein E. Classification and prediction of smoking relapse episodes: An exploration of individual differences. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1988;56:104–110. - PubMed
-
- Bartoshuk LM. Comparing sensory experiences across individuals: Recent psychophysical advances illuminate genetic variation in taste perception. Chemical Senses. 2002;25:447–460. - PubMed
-
- Bohn MJ, Krahn DD, Staehler BA. Development and initial validation of a measure of drinking urges in abstinent alcoholics. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1995;19:600–606. - PubMed
-
- Brandon TH, Tiffany ST, Obremski KM, Baker TB. Postcessation cigarette use: The process of relapse. Addictive Behaviors. 1990;15:105–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

