Neural mechanism for stochastic behaviour during a competitive game
- PMID: 17015181
- PMCID: PMC1752206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2006.05.044
Neural mechanism for stochastic behaviour during a competitive game
Abstract
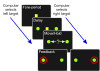
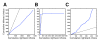
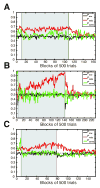
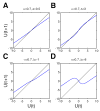
Previous studies have shown that non-human primates can generate highly stochastic choice behaviour, especially when this is required during a competitive interaction with another agent. To understand the neural mechanism of such dynamic choice behaviour, we propose a biologically plausible model of decision making endowed with synaptic plasticity that follows a reward-dependent stochastic Hebbian learning rule. This model constitutes a biophysical implementation of reinforcement learning, and it reproduces salient features of behavioural data from an experiment with monkeys playing a matching pennies game. Due to interaction with an opponent and learning dynamics, the model generates quasi-random behaviour robustly in spite of intrinsic biases. Furthermore, non-random choice behaviour can also emerge when the model plays against a non-interactive opponent, as observed in the monkey experiment. Finally, when combined with a meta-learning algorithm, our model accounts for the slow drift in the animal's strategy based on a process of reward maximization.
Figures
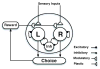
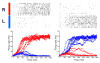
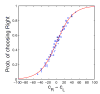
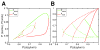
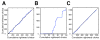
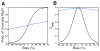
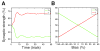
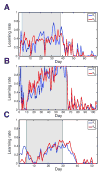
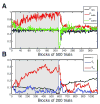
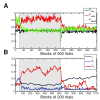
Comment in
-
Classic Hebbian learning endows feed-forward networks with sufficient adaptability in challenging reinforcement learning tasks.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Jun 1;125(6):2034-2037. doi: 10.1152/jn.00712.2020. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33909499
Similar articles
-
Reinforcement learning and decision making in monkeys during a competitive game.Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2004 Dec;22(1):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.07.007. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15561500
-
Self-control with spiking and non-spiking neural networks playing games.J Physiol Paris. 2010 May-Sep;104(3-4):108-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2009.11.013. Epub 2009 Nov 26. J Physiol Paris. 2010. PMID: 19944157
-
Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game.Nat Neurosci. 2004 Apr;7(4):404-10. doi: 10.1038/nn1209. Epub 2004 Mar 7. Nat Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15004564
-
[Neural mechanisms of decision making].Brain Nerve. 2008 Sep;60(9):1017-27. Brain Nerve. 2008. PMID: 18807936 Review. Japanese.
-
Valuation of uncertain and delayed rewards in primate prefrontal cortex.Neural Netw. 2009 Apr;22(3):294-304. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2009.03.010. Epub 2009 Mar 29. Neural Netw. 2009. PMID: 19375276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reinforcement learning: Computational theory and biological mechanisms.HFSP J. 2007 May;1(1):30-40. doi: 10.2976/1.2732246/10.2976/1. Epub 2007 May 8. HFSP J. 2007. PMID: 19404458 Free PMC article.
-
Neural substrates of cognitive biases during probabilistic inference.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 26;7:11393. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11393. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27116102 Free PMC article.
-
Neural basis of reinforcement learning and decision making.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:287-308. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150512. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22462543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feature-based learning improves adaptability without compromising precision.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 24;8(1):1768. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01874-w. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29170381 Free PMC article.
-
Fast adaptation to rule switching using neuronal surprise.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Feb 20;20(2):e1011839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011839. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38377112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amit DJ, Fusi S. Dynamic learning in neural networks with material synapses. Neural Computation. 1994;6:957–982.
-
- Bar-Hillel M, Wagenaar WA. The perception of randomness. Advances in Applied Mathematics. 1991;12:428–454.
-
- Barraclough DJ, Conroy ML, Lee D. Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nature Neuroscience. 2004;7:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Berns GS, Sejnowski TJ. A computational model of how the basal ganglia produce sequences. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 1998;10:108–121. - PubMed
-
- Brunel N, Wang XJ. Effects of neuromodulation in a cortical network model of object working memory dominated by recurrent inhibition. Journal of Computational Neuroscience. 2001;11:63–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

