Mechanisms of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 17015228
- PMCID: PMC1810425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.021
Mechanisms of neuropathic pain
Abstract
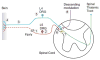
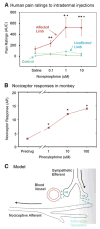
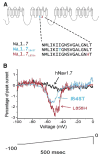
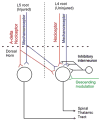
Neuropathic pain refers to pain that originates from pathology of the nervous system. Diabetes, infection (herpes zoster), nerve compression, nerve trauma, "channelopathies," and autoimmune disease are examples of diseases that may cause neuropathic pain. The development of both animal models and newer pharmacological strategies has led to an explosion of interest in the underlying mechanisms. Neuropathic pain reflects both peripheral and central sensitization mechanisms. Abnormal signals arise not only from injured axons but also from the intact nociceptors that share the innervation territory of the injured nerve. This review focuses on how both human studies and animal models are helping to elucidate the mechanisms underlying these surprisingly common disorders. The rapid gain in knowledge about abnormal signaling promises breakthroughs in the treatment of these often debilitating disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Ahlgren SC, Levine JD. Mechanical hyperalgesia in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Neuroscience. 1993;52:1049–1055. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Ringkamp M, Hartke TV, Chien HF, Flavahan NA, Campbell JN, Meyer RA. Uninjured C-fiber nociceptors develop spontaneous activity and alpha adrenergic sensitivity following L6 spinal nerve ligation in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:455–466. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Raja SN, Wesselmann U, Fuchs PN, Meyer RA, Campbell JN. Intradermal injection of norepinephrine evokes pain in patients with sympathetically maintained pain. Pain. 2000;88:161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

