Structural basis for understanding oncogenic p53 mutations and designing rescue drugs
- PMID: 17015838
- PMCID: PMC1635156
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607286103
Structural basis for understanding oncogenic p53 mutations and designing rescue drugs
Abstract
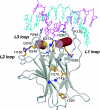
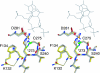
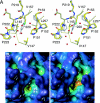
The DNA-binding domain of the tumor suppressor p53 is inactivated by mutation in approximately 50% of human cancers. We have solved high-resolution crystal structures of several oncogenic mutants to investigate the structural basis of inactivation and provide information for designing drugs that may rescue inactivated mutants. We found a variety of structural consequences upon mutation: (i) the removal of an essential contact with DNA, (ii) creation of large, water-accessible crevices or hydrophobic internal cavities with no other structural changes but with a large loss of thermodynamic stability, (iii) distortion of the DNA-binding surface, and (iv) alterations to surfaces not directly involved in DNA binding but involved in domain-domain interactions on binding as a tetramer. These findings explain differences in functional properties and associated phenotypes (e.g., temperature sensitivity). Some mutants have the potential of being rescued by a generic stabilizing drug. In addition, a mutation-induced crevice is a potential target site for a mutant-selective stabilizing drug.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
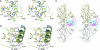
References
-
- Vogelstein B., Lane D, Levine AJ. Nature. 2000;408:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Lu X. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:594–604. - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, Eeles R, Hollstein M, Khan MA, Harris CC, Hainaut P. Hum Mutat. 2002;19:607–614. - PubMed
-
- Beroud C, Soussi T. Hum Mutat. 2003;21:176–181. - PubMed
-
- Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP. Science. 1994;265:346–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

