Modulation of the function of presynaptic alpha7 and non-alpha7 nicotinic receptors by the tryptophan metabolites, 5-hydroxyindole and kynurenate in mouse brain
- PMID: 17016503
- PMCID: PMC2014664
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706914
Modulation of the function of presynaptic alpha7 and non-alpha7 nicotinic receptors by the tryptophan metabolites, 5-hydroxyindole and kynurenate in mouse brain
Abstract
Background and purpose: Two metabolites of tryptophan, 5-hydroxyindole and kynurenic acid (kynurenate) affect the function of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), as measured by electrophysiological and Ca2+ fluorescence techniques. To better understand the modulations by 5-hydroxyindole and kynurenate of the function of nAChR subtypes, we compared the effects of 5-hydroxyindole and kynurenate on the release of various transmitters evoked by nAChR activation.
Experimental approach: The function of alpha7nAChRs located on glutamatergic terminals was investigated by monitoring the release of [3H]D-aspartate or of endogenous glutamate from neocortical synaptosomes. We also comparatively considered non-alpha7 release-enhancing nAChRs localized on hippocampal noradrenergic or cholinergic terminals, as well as on striatal dopaminergic terminals.
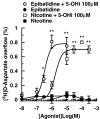
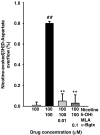
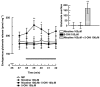
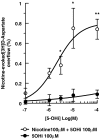
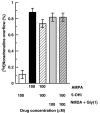
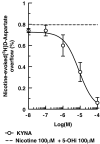
Key results: Epibatidine or nicotine, inactive on their own on basal release, enhanced [3H]D- aspartate and glutamate efflux in presence of 5-hydroxyindole. The release evoked by nicotine plus 5-hydroxyindole was abolished by methyllycaconitine or alpha-bungarotoxin. Presynaptic nAChRs mediating the release of [3H]noradrenaline ([3H]NA), [3H]dopamine ([3H]DA), or [3H]ACh were inhibited by 5-OHi. The alpha7nAChR-mediated release of [3H]D-aspartate was reduced by kynurenate at concentrations unable to affect the non-alpha7 receptor-mediated release of tritiated NA, DA or ACh.
Conclusions and implications: (i) 5-hydroxyindole permits selective activation of alpha7nAChRs mediating glutamate release; (ii) kynurenate down-regulates the permissive role of 5-hydroxyindole on alpha7nAChR activation; (iii) the non-alpha7nAChRs mediating release of NA, DA or ACh can be inhibited by 5-hydroxyindole, but not by kynurenate. These findings suggest up the possibility of developing novel drugs able to modulate selectively the cholinergic-glutamatergic transmission.
Figures

References
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EFR, Yu P, Arruda EZ, Almeida LEF, Guidetti P, et al. Targeted deletion of the kynurenine aminotransferase II gene reveals a critical role of endogenous kynurenic acid in the regulation of synaptic transmission via α7 nicotinic receptors in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2004;24:4635–4648. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baran H, Jellinger K, Deecke L. Kynurenine metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm. 1999;106:165–181. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Matson WR, Storey E, Milbury P, Ryan EA, Ogawa T, et al. Kynurenic acid concentrations are reduced in Huntington's disease cerebral cortex. J Neurol Sci. 1992;108:80–87. - PubMed
-
- Court J, Martin-Ruiz C, Piggott M, Spurden D, Griffiths M, Perry E. Nicotinic receptor abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49:175–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

