Myeloid suppressor cells regulate the adaptive immune response to cancer
- PMID: 17016554
- PMCID: PMC1578609
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29906
Myeloid suppressor cells regulate the adaptive immune response to cancer
Abstract
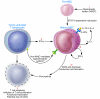
Inflammation resultant from tumor growth, infection with certain pathogens, or in some cases, trauma, can result in systemic release of cytokines, especially GM-CSF, that in turn stimulate the abundant production and activation of a population of immature myeloid cells, termed myeloid suppressor cells (MSCs), that have potent immunosuppressive functions. In this issue of the JCI, Gallina and colleagues have illuminated some complex issues concerning the development, activation, and function of MSCs (see the related article beginning on page 2777). They show that activation of MSCs is initiated in response to IFN-gamma, presumably produced in situ by antitumor T cells in the tumor microenvironment. After this triggering event, MSCs express 2 enzymes involved in l-arginine metabolism, Arginase I and iNOS, whose metabolic products include diffusible and highly reactive peroxynitrites, the ultimate biochemical mediators of T cell immune suppression. The multifaceted regulation of this complex suppressive effector system provides several potential therapeutic targets.
Figures
Comment on
-
Tumors induce a subset of inflammatory monocytes with immunosuppressive activity on CD8+ T cells.J Clin Invest. 2006 Oct;116(10):2777-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI28828. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17016559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- North R. Down-regulation of the antitumor immune response. Adv. Cancer Res. 1985;45:1–42. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi T., Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in immune surveillance and treatment of cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006;16:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Dunn G.P., Bruce A.T., Ikeda H., Old L.J., Schreiber R.D. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:991–998. - PubMed
-
- Frey A.B., Monu N. Effector-phase tolerance: another mechanism of how cancer escapes antitumor immune response. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006;79:652–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

