Transcriptional profiling of the cell cycle checkpoint gene krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a global inhibitory function in macromolecular biosynthesis
- PMID: 17017123
- PMCID: PMC1626270
- DOI: 10.3727/000000006783991908
Transcriptional profiling of the cell cycle checkpoint gene krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a global inhibitory function in macromolecular biosynthesis
Abstract
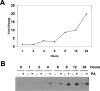
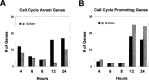
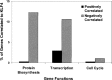
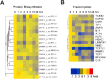
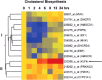
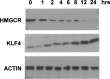
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4; also known as gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor or GKLF) is known to exhibit checkpoint function during the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle. The mechanism by which KLF4 exerts these effects is not fully established. Here we investigated the expression profile of KLF4 in an inducible system over a time course of 24 h. Using oligonucleotide microarrays, we determined that the fold changes relative to control in expression levels of KLF4 exhibited a time-dependent increase from 3- to 20-fold between 4 and 24 h following KLF4 induction. During this period and among a group of 473 cell cycle regulatory genes examined, 96 were positively correlated and 86 were negatively correlated to KLF4's expression profile. Examples of upregulated cell cycle genes include those encoding tumor suppressors such as MCC and FHIT, and cell cycle inhibitors such as CHES1 and CHEK1. Examples of downregulated genes include those that promote the cell cycle including several cyclins and those required for DNA replication. Unexpectedly, several groups of genes involved in macromolecular synthesis, including protein biosynthesis, transcription, and cholesterol biosynthesis, were also significantly inhibited by KLF4. Thus, KLF4 exerts a global inhibitory effect on macromolecular biosynthesis that is beyond its established role as a cell cycle inhibitor.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Z. Y.; Shie J.; Tseng C. Up-regulation of gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor by interferon-gamma in human colon carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 477:67–72; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Dang D. T.; Bachman K. E.; Mahatan C. S.; Dang L. H.; Giardiello F. M.; Yang V. W. Decreased expression of the gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor gene in intestinal adenomas of multiple intestinal neoplasia mice and in colonic adenomas of familial adenomatous polyposis patients. FEBS Lett. 476:203–207; 2000. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
