Levels and distribution of BCNU in GBM tumors following intratumoral injection of DTI-015 (BCNU-ethanol)
- PMID: 17018699
- PMCID: PMC1828109
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2006-014
Levels and distribution of BCNU in GBM tumors following intratumoral injection of DTI-015 (BCNU-ethanol)
Abstract
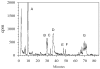
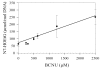
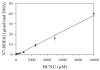
The alkylation products formed by in vitro treatment of DNA with tritium-labeled 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea ((3)H-BCNU) were identified and quantified. Twelve adducts were resolved by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The principal DNA adducts formed by BCNU treatment corresponded to N-7-(2-hydroxyethyl)guanine (N7-HOEtG) (26%), N-7-(2-chloroethyl)guanine (15%), and phosphotriesters (19%). In addition, several minor products were identified as 1,2-(diguan-7-yl)ethane, N-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-deoxyguanosine, 1-(N-1-2-deoxyguanosinyl), 2-(N-3-2-deoxycytidyl)ethane cross-link, and O-6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-deoxyguanosine, and individually they represented 1% to 5% of the total alkylation. An HPLC-electrochemical method was applied to quantify the levels of N7-HOEtG in samples treated with BCNU. Treatment of either purified DNA or U87MG cells with various amounts of BCNU produced a linear increase in the amount of N7-HOEtG. These results demonstrated that the levels of N7-HOEtG formed by BCNU treatment could be used as a molecular dosimeter of BCNU treatment dose. We measured the levels of N7-HOEtG in DNA isolated from tumor samples taken from four patients with GBM tumors following stereotactic intratumoral injection with DTI-015 (BCNU-ethanol). The level of N7-HOEtG in these samples ranged from 14.7 to 121.9 micromol N7-HOETG/mol DNA within 1 cm of the site of injection. As the distance from the site of injection increased, the levels of N7-HOEtG in tumor DNA decreased. In two of the samples, the levels of N7-HOEtG were 0.2 to 0.3 micromol N7-HOETG/mol DNA at 3.5 to 3.9 cm from the site of injection, demonstrating significant distribution of BCNU in the tumor. The levels of N7-HOEtG in these tumor samples corresponded to BCNU treatment concentrations of 0.02 to 43.0 mM. These studies demonstrate that stereotactic intratumoral injection of DTI-015 into human GBM tumors produces high concentrations of BCNU up to 2.5 cm from the site of injection in some of the tumors. These observations suggest that intratumoral injection of DTI-015 may be of benefit in the treatment of primary and recurrent GBM tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Bergenheim AT, Capala J, Roslin M, Henriksson R. Distribution of BPA and metabolic assessment in glioblastoma patients during BNCT treatment: A microdialysis study. J Neurooncol. 2005;71:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Blasberg RG, Patlak C, Fenstermacher JD. Intrathecal chemotherapy: Brain tissue profiles after ventriculocisternal perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975;195:73–83. - PubMed
-
- Bodell WJ. Effect of cations on the formation of DNA alkylation products in DNA reacted with 1-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Chem Res Toxicol. 1999;12:965–970. - PubMed
-
- Bodell WJ, Tokuda K, Ludlum DB. Differences in DNA alkylation products formed in sensitive and resistant glioma cells treated with N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 1988;48:4489–4492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

