Preformed antibody, not primed T cells, is the initial and major barrier to bone marrow engraftment in allosensitized recipients
- PMID: 17018854
- PMCID: PMC1785137
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-022772
Preformed antibody, not primed T cells, is the initial and major barrier to bone marrow engraftment in allosensitized recipients
Abstract
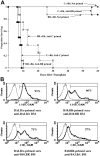
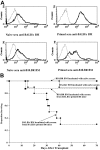
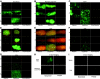
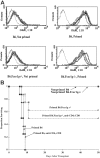
Multiply-transfused individuals are at higher risk for BM rejection. We show that whereas allosensitization resulted in the priming of both cellular and humoral immunity, preformed antibody was the major barrier to engraftment. The generation of cross-reactive alloantibody led to rejection of BM of a different MHC-disparate strain. Imaging studies indicated that antibody-mediated rejection was very rapid (<3 hours) in primed recipients, while T-cell-mediated rejection in nonprimed mice took more than 6 days. Antibody-mediated BM rejection was not due to a defect in BM homing as rejection occurred despite direct intra-BM infusion of donor BM. Rejection was dependent upon host FcR+ cells. BM cells incubated with serum from primed mice were eliminated in nonprimed recipients, indicating that persistent exposure to high-titer antibody was not essential for rejection. High donor engraftment was achieved in a proportion of primed mice by mega-BM cell dose, in vivo T-cell depletion, and high-dose immunoglobulin infusion. The addition of splenectomy to this protocol only modestly added to the efficacy of this combination strategy. These data demonstrate both rapid alloantibody-mediated elimination of BM by host FcR+ cells and priming of host antidonor T cells and suggest a practical strategy to overcome engraftment barriers in primed individuals.
Figures

Comment in
-
B cells versus T cells as primary barrier to hematopoietic engraftment in allosensitized recipients.Blood. 2009 Jan 29;113(5):1205. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-177436. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19179478 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Warren RP, Storb R, Weiden PL, Mickelson EM, Thomas ED. Direct and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against HLA identical sibling lymphocytes: correlation with marrow graft rejections. Transplantation. 1976;22:631–635. - PubMed
-
- Anasetti C, Doney KC, Storb R, et al. Marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: long-term outcome in fifty “untransfused” patients. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104:461–466. - PubMed
-
- Anasetti C, Amos D, Beatty PG, et al. Effect of HLA compatibility on engraftment of bone marrow transplants in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:197–204. - PubMed
-
- Barge AJ, Johnson G, Witherspoon R, Torok-Storb B. Antibody-mediated marrow failure after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1989;74:1477–1480. - PubMed
-
- Warren RP, Storb R, Weiden PL, Su PJ, Thomas ED. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in patients with aplastic anemia: distinguishing transfusion-induced sensitization from possible immune-mediated aplastic anemia. Transplant Proc. 1981;13:245–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

