Experimental analysis and treatment of multiply controlled problem behavior: a systematic replication and extension
- PMID: 17020218
- PMCID: PMC1702396
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2006.170-04
Experimental analysis and treatment of multiply controlled problem behavior: a systematic replication and extension
Abstract
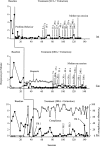
We evaluated interventions designed to reduce multiply controlled problem behavior exhibited by a young boy with developmental disabilities, using a multiple baseline design. Each intervention was designed to address a specific social function of problem behavior. Results showed that the separate interventions were useful in reducing problem behavior, and terminal schedules were reached by way of schedule thinning (attention condition) and delays to reinforcement (tangible and escape conditions).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreasing disruptive behavior by adolescent boys in residential care by increasing their positive to negative interactional ratios.Behav Modif. 1997 Oct;21(4):470-86. doi: 10.1177/01454455970214005. Behav Modif. 1997. PMID: 9337602
-
Reinforcement magnitude: an evaluation of preference and reinforcer efficacy.J Appl Behav Anal. 2008 Summer;41(2):203-20. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2008.41-203. J Appl Behav Anal. 2008. PMID: 18595284 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of differential negative reinforcement of other behavior and noncontingent escape on compliance.J Appl Behav Anal. 2003 Fall;36(3):379-82. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2003.36-379. J Appl Behav Anal. 2003. PMID: 14596581 Free PMC article.
-
[Dialectical behavior therapy approaches with disruptive behavior disorders].Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2016 Nov;44(6):443-454. doi: 10.1024/1422-4917/a000478. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2016. PMID: 27642799 Review. German.
-
Noncontingent reinforcement is an empirically supported treatment for problem behavior exhibited by individuals with developmental disabilities.Res Dev Disabil. 2009 Jan-Feb;30(1):44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2008.03.002. Epub 2008 May 7. Res Dev Disabil. 2009. PMID: 18467073 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of behavioral intervention and sensory-integration therapy in the treatment of challenging behavior.J Autism Dev Disord. 2011 Oct;41(10):1303-20. doi: 10.1007/s10803-010-1149-x. J Autism Dev Disord. 2011. PMID: 21161577
-
Treating Individuals With Intellectual Disabilities and Challenging Behaviors With Adapted Dialectical Behavior Therapy.J Ment Health Res Intellect Disabil. 2013 Oct;6(4):280-303. doi: 10.1080/19315864.2012.700684. J Ment Health Res Intellect Disabil. 2013. PMID: 23914278 Free PMC article.
-
Practice Recommendations for Addressing Problem Behaviors in Siblings with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Behav Anal Pract. 2017 May 17;10(4):363-374. doi: 10.1007/s40617-017-0190-z. eCollection 2017 Dec. Behav Anal Pract. 2017. PMID: 29214132 Free PMC article.
-
Single-case experimental designs: a systematic review of published research and current standards.Psychol Methods. 2012 Dec;17(4):510-50. doi: 10.1037/a0029312. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Psychol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22845874 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Changes in Preference for Schedule-Thinning Arrangements as a Function of Relative Reinforcement Density.Behav Modif. 2018 Jul;42(4):472-497. doi: 10.1177/0145445517742883. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Behav Modif. 2018. PMID: 29182009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borrero C.S.W, Vollmer T.R, Borrero J.C, Bourret J. A method for evaluating parameters of reinforcement during parent-child interactions. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2005;26:503–600. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

