Multiple signaling pathways regulate the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1
- PMID: 17020917
- PMCID: PMC1636490
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl712
Multiple signaling pathways regulate the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1
Abstract
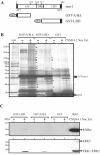
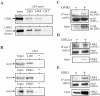
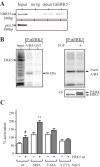
The orphan nuclear receptor nurr1 (NR4A2) is an essential transcription factor for the acquisition and maintenance of the phenotype of dopamine (DA)-synthesizing neurons in the mesencephalon. Although structurally related to ligand-regulated nuclear receptors, nurr1 is functionally atypical due to its inability to bind a cognate ligand and to activate transcription following canonical nuclear receptor (NR) rules. Importantly, the physiological stimuli that activate this NR and the signaling proteins that regulate its transcriptional activity in mesencephalic neurons are unknown. We used an affinity chromatography approach and CSM14.1 cells of mesencephalic origin to isolate and identify several proteins that interact directly with nurr1 and regulate its transcriptional activity. Notably, we demonstrate that the mitogen-activated protein kinases, ERK2 and ERK5, elevate, whereas LIM Kinase 1 inhibits nurr1 transcriptional activity. Furthermore, nurr1 recruits ERK5 to a NBRE-containing promoter and is a potential substrate for this kinase. We have identified amino acids in the A/B domain of nurr1 important for mediating the ERK5 activating effects on nurr1 transcriptional activity. Our results suggest that nurr1 acts as a point of convergence for multiple signaling pathways that likely play a critical role in differentiation and phenotypic expression of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Initiation of dopaminergic differentiation of Nurr1(-) mesencephalic precursor cells depends on activation of multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.Stem Cells. 2009 Aug;27(8):2009-21. doi: 10.1002/stem.122. Stem Cells. 2009. PMID: 19544469
-
The glucocorticoid receptor is a co-regulator of the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1.J Neurochem. 2008 Feb;104(3):777-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05055.x. Epub 2007 Nov 6. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 17986226
-
Nurr1 is phosphorylated by ERK2 in vitro and its phosphorylation upregulates tyrosine hydroxylase expression in SH-SY5Y cells.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Aug 16;423(2):118-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.06.041. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17681692
-
Nurr1, an orphan nuclear receptor with essential functions in developing dopamine cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2004 Oct;318(1):45-52. doi: 10.1007/s00441-004-0974-7. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Cell Tissue Res. 2004. PMID: 15340833 Review.
-
The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.001. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16243425 Review.
Cited by
-
Nurr1 Is Not an Essential Regulator of BDNF in Mouse Cortical Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 20;23(12):6853. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126853. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743300 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Aspects of LIMK Regulation and Pharmacology.Cells. 2022 Jan 2;11(1):142. doi: 10.3390/cells11010142. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining mechanisms of actin polymerization and depolymerization during dendritic spine morphogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2009 Apr 20;185(2):323-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200809046. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19380880 Free PMC article.
-
1,1-Bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl)methane activates the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 and inhibits bladder cancer growth.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Dec;7(12):3825-33. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0730. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 19074857 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Developmental Toxicants using Human Embryonic Stem Cells.Toxicol Res. 2013 Dec 31;29(4):221-7. doi: 10.5487/TR.2013.29.4.221. Toxicol Res. 2013. PMID: 24578791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Girault J.A., Greengard P. The neurobiology of dopamine signalling. Arch. Neurol. 2004;61:641–644. - PubMed
-
- Law S.W., Conneely O.M., Demayo F.J., O'Malley B.W. Identification of a new brain-specific transcription factor, NURR1. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992;6:2129–2135. - PubMed
-
- Zetterstrom R.H., Williams R., Perlmann T., Olson L. Cellular expression of the immediate early transcription factors Nurr1 and NGFI-B suggests a gene regulatory role in several brain regions including the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1996;41:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Zetterstrom R.H., Solomin L., Jansson L., Hoffer B.J., Olson L., Perlmann T. Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science. 1997;276:248–250. - PubMed
-
- Castillo S.O., Baffi J.S., Palkovits M., Goldstein D.S., Kopin I.J., Witta J., Magnuson M.A., Nikodem V.M. Dopamine biosynthesis is selectively abolished in substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area but not in hypothalamic neurons in mice with targeted disruption of the Nurr1 gene. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998;11:36–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

