Multiple signaling pathways regulate the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1
- PMID: 17020917
- PMCID: PMC1636490
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl712
Multiple signaling pathways regulate the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1
Abstract
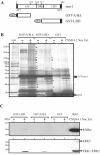
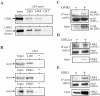
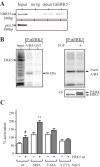
The orphan nuclear receptor nurr1 (NR4A2) is an essential transcription factor for the acquisition and maintenance of the phenotype of dopamine (DA)-synthesizing neurons in the mesencephalon. Although structurally related to ligand-regulated nuclear receptors, nurr1 is functionally atypical due to its inability to bind a cognate ligand and to activate transcription following canonical nuclear receptor (NR) rules. Importantly, the physiological stimuli that activate this NR and the signaling proteins that regulate its transcriptional activity in mesencephalic neurons are unknown. We used an affinity chromatography approach and CSM14.1 cells of mesencephalic origin to isolate and identify several proteins that interact directly with nurr1 and regulate its transcriptional activity. Notably, we demonstrate that the mitogen-activated protein kinases, ERK2 and ERK5, elevate, whereas LIM Kinase 1 inhibits nurr1 transcriptional activity. Furthermore, nurr1 recruits ERK5 to a NBRE-containing promoter and is a potential substrate for this kinase. We have identified amino acids in the A/B domain of nurr1 important for mediating the ERK5 activating effects on nurr1 transcriptional activity. Our results suggest that nurr1 acts as a point of convergence for multiple signaling pathways that likely play a critical role in differentiation and phenotypic expression of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons.
Figures



References
-
- Girault J.A., Greengard P. The neurobiology of dopamine signalling. Arch. Neurol. 2004;61:641–644. - PubMed
-
- Law S.W., Conneely O.M., Demayo F.J., O'Malley B.W. Identification of a new brain-specific transcription factor, NURR1. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992;6:2129–2135. - PubMed
-
- Zetterstrom R.H., Williams R., Perlmann T., Olson L. Cellular expression of the immediate early transcription factors Nurr1 and NGFI-B suggests a gene regulatory role in several brain regions including the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1996;41:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Zetterstrom R.H., Solomin L., Jansson L., Hoffer B.J., Olson L., Perlmann T. Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science. 1997;276:248–250. - PubMed
-
- Castillo S.O., Baffi J.S., Palkovits M., Goldstein D.S., Kopin I.J., Witta J., Magnuson M.A., Nikodem V.M. Dopamine biosynthesis is selectively abolished in substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area but not in hypothalamic neurons in mice with targeted disruption of the Nurr1 gene. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998;11:36–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

