A stochastic framework for evaluating seizure prediction algorithms using hidden Markov models
- PMID: 17021032
- PMCID: PMC2230664
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00190.2006
A stochastic framework for evaluating seizure prediction algorithms using hidden Markov models
Abstract
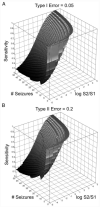
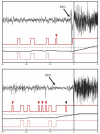
Responsive, implantable stimulation devices to treat epilepsy are now in clinical trials. New evidence suggests that these devices may be more effective when they deliver therapy before seizure onset. Despite years of effort, prospective seizure prediction, which could improve device performance, remains elusive. In large part, this is explained by lack of agreement on a statistical framework for modeling seizure generation and a method for validating algorithm performance. We present a novel stochastic framework based on a three-state hidden Markov model (HMM) (representing interictal, preictal, and seizure states) with the feature that periods of increased seizure probability can transition back to the interictal state. This notion reflects clinical experience and may enhance interpretation of published seizure prediction studies. Our model accommodates clipped EEG segments and formalizes intuitive notions regarding statistical validation. We derive equations for type I and type II errors as a function of the number of seizures, duration of interictal data, and prediction horizon length and we demonstrate the model's utility with a novel seizure detection algorithm that appeared to predicted seizure onset. We propose this framework as a vital tool for designing and validating prediction algorithms and for facilitating collaborative research in this area.
Figures

References
-
- Albert PS. A two-state Markov mixture model for a time-series of epileptic seizure counts. Biometrics. 1991;47:1371–1381. - PubMed
-
- Andrzejak RG, Mormann F, Kreuz T, Rieke C, Kraskov A, Elger C, Lehnertz K. Testing the null hypothesis of the nonexistence of a preseizure state. Phys Rev E. 2003;67:010901. - PubMed
-
- Andrzejak RG, Widman G, Lehnertz K, Rieke C, David P, Elger CE. The epileptic process as nonlinear deterministic dynamics in a stochastic environment: an evaluation on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2001;44:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Aschenbrenner-Scheibe R, Maiwald T, Winterhalder M, Voss HU, Timmer J, Schulze-Bonhage A. How well can epileptic seizures be predicted? An evaluation of a nonlinear method. Brain. 2003;126:2616–2626. - PubMed
-
- Dempster AP, Laird N, Rubin DB. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc B. 1977;39:1–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

