Performance of the genotype MTBDR line probe assay for detection of resistance to rifampin and isoniazid in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with low- and high-level resistance
- PMID: 17021094
- PMCID: PMC1594786
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01054-06
Performance of the genotype MTBDR line probe assay for detection of resistance to rifampin and isoniazid in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with low- and high-level resistance
Abstract
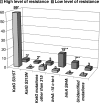
We assessed the performance of the Genotype MTBDR line probe assay that offers the simultaneous identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its resistance to rifampin (RIF) and isoniazid (INH) by detecting the most commonly found mutations in the rpoB and katG genes. One hundred thirteen M. tuberculosis isolates were tested. The nucleotide sequences of the katG and inhA genes and the mabA-inhA promoter region were also determined. The MTBDR assay detected 100% and 67% (n = 64) of the strains resistant to RIF and INH, respectively. Among the latter, 62 strains carried a Ser315Thr mutation in katG, 59 of them displaying a high level of resistance to INH. Two strains with a low level of INH resistance had a Ser315Asn mutation. No mutation was found by the MTBDR assay for 31 INH-resistant strains (33%), of which 24 showed a low level of resistance. By DNA sequencing, we found among them various mutations in the KatG protein for 7 strains, a C-->T mutation in position -15 of the mabA-inhA promoter in 17 strains, and a Ser94Ala mutation in InhA for 7 strains. In conclusion, the MTBDR assay, which fits easily in the workflow of a routine laboratory, enabled the detection of 100% of the RIF-resistant strains and 89% of the INH-resistant strains with a high level of resistance but only 17% of the strains characterized by a low level of INH resistance, indicating that the test can be used as a rapid method to detect in the same experiment the rifampin-resistant and the high-level isoniazid-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis.
Figures
References
-
- Baker, L. V., T. J. Brown, O. Maxwell, A. L. Gibson, Z. Fang, M. D. Yates, and F. A. Drobniewski. 2005. Molecular analysis of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from England and Wales reveals the phylogenetic significance of the ahpC −46A polymorphism. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49:1455-1464. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, A., E. Dubnau, A. Quemard, V. Balasubramanian, K. S. Um, T. Wilson, D. Collins, G. de Lisle, and W. R. Jacobs, Jr. 1994. inhA, a gene encoding a target for isoniazid and ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 263:227-230. - PubMed
-
- Canetti, G., N. Rist, and J. Grosset. 1963. Measurement of sensitivity of the tuberculous bacillus to antibacillary drugs by the method of proportions. Methodology, resistance criteria, results and interpretation. Rev. Tuberc. Pneumol. (Paris) 27:217-272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

