Osteomyelitis of the ulna caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis
- PMID: 17021123
- PMCID: PMC1594789
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00793-06
Osteomyelitis of the ulna caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis
Abstract
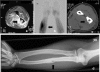
A 41-year-old man was provided with a jacket crown after a root end resection of a molar. Four months later, cortical destruction of the ulnar diaphysis with swelling and pain appeared in his forearm. No microorganism could be grown from an intraoperative tissue specimen, but bacterial 16S rRNA genes were detected by broad-range PCR, revealing Porphyromonas gingivalis as the causative agent of osteomyelitis.
Figures
References
-
- Amornchat, C., S. Rassameemasmaung, W. Scripairojthikoon, and S. Swasdison. 2003. Invasion of Porphyromonas gingivalis into human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 5:98-105. - PubMed
-
- Cortelli, J. R., S. C. Cortelli, S. Jordan, V. I. Haraszthy, and J. J. Zambon. 2005. Prevalence of periodontal pathogens in Brazilians with aggressive or chronic periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 32:860-866. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande, R. G., M. Khan, and C. A. Genco. 1998. 1999. Invasion strategies of the oral pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis: implications for cardiovascular disease. Invasion Metastasis 18:57-69. - PubMed
-
- Foster, N., J. Cheetham, J. J. Taylor, and P. M. Preshaw. 2005. VIP inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS-induced immune responses in human monocytes. J. Dent. Res. 84:999-1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

