Age-independent synaptogenesis by phosphoinositide 3 kinase
- PMID: 17021175
- PMCID: PMC6674615
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1223-06.2006
Age-independent synaptogenesis by phosphoinositide 3 kinase
Abstract
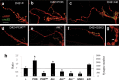
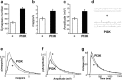
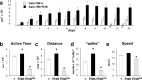
Synapses are specialized communication points between neurons, and their number is a major determinant of cognitive abilities. These dynamic structures undergo developmental- and activity-dependent changes. During brain aging and certain diseases, synapses are gradually lost, causing mental decline. It is, thus, critical to identify the molecular mechanisms controlling synapse number. We show here that the levels of phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) regulate synapse number in both Drosophila larval motor neurons and adult brain projection neurons. The supernumerary synapses induced by PI3K overexpression are functional and elicit changes in behavior. Remarkably, PI3K activation induces synaptogenesis in aged adult neurons as well. We demonstrate that persistent PI3K activity is necessary for synapse maintenance. We also report that PI3K controls the expression and localization of synaptic markers in human neuroblastoma cells, suggesting that PI3K synaptogenic activity is conserved in humans. Thus, we propose that PI3K stimulation can be applied to prevent or delay synapse loss in normal aging and in neurological disorders.
Figures

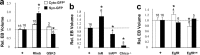
Similar articles
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase activation controls synaptogenesis and spinogenesis in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 23;31(8):2721-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4477-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21414895 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic PI3K activity triggers the formation of glutamate receptors at neuromuscular terminals of Drosophila.J Cell Sci. 2012 Aug 1;125(Pt 15):3621-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102806. Epub 2012 Apr 14. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22505608
-
Axon length maintenance and synapse integrity are regulated by c-AMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) during larval growth of the drosophila sensory neurons.J Neurogenet. 2019 Sep;33(3):157-163. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2019.1586896. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Neurogenet. 2019. PMID: 30955404
-
At a PI3K crossroads: lessons from flies and rodents.Rev Neurosci. 2012;23(1):29-37. doi: 10.1515/rns.2011.057. Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22718611 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of synaptogenesis.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Sep 13;14:939793. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.939793. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36176941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Insulin Signaling Targeted to Serotonergic Neurons but Not Other Neuronal Subtypes Extends Lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 5;14:893444. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.893444. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35865744 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct sets of FGF receptors sculpt excitatory and inhibitory synaptogenesis.Development. 2015 May 15;142(10):1818-30. doi: 10.1242/dev.115568. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Development. 2015. PMID: 25926357 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal α7 nicotinic ACh receptors modulate presynaptic NMDA receptor expression and structural plasticity of glutamatergic presynaptic boutons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 21;107(38):16661-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007397107. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20817852 Free PMC article.
-
Synapse loss in olfactory local interneurons modifies perception.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 23;31(8):2734-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5046-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21414896 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog, deleted on chromosome 10 deficiency in brain causes defects in synaptic structure, transmission and plasticity, and myelination abnormalities.Neuroscience. 2008 Jan 24;151(2):476-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.10.048. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18082964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal-Mawal A, Qureshi HY, Cafferty PW, Yuan Z, Han D, Lin R, Paudel HK. 14–3-3 connects glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta to tau within a brain microtubule-associated tau phosphorylation complex. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:12722–12728. - PubMed
-
- Arendt T, Gartner U, Seeger G, Barmashenko G, Palm K, Mittmann T, Yan L, Hummeke M, Behrbohm J, Bruckner MK, Holzer M, Wahle P, Heumann R. Neuronal activation of Ras regulates synaptic connectivity. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19:2953–2966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
