Development of novel immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM enzyme immunoassays based on recombinant Puumala and Dobrava hantavirus nucleocapsid proteins
- PMID: 17021245
- PMCID: PMC1694442
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00208-06
Development of novel immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM enzyme immunoassays based on recombinant Puumala and Dobrava hantavirus nucleocapsid proteins
Abstract
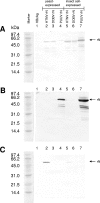
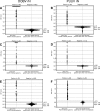
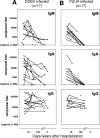
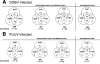
Human infections with Asian and European hantaviruses can result in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndromes of differing severities characterized by renal dysfunction and sometimes by pulmonary symptoms. For the serological detection of human infections by hantaviruses relevant for Europe, we developed monoclonal antibody capture immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) based on yeast-expressed nucleocapsid proteins of Puumala and Dobrava hantaviruses. Moreover, for diagnosis of acute infections, mu-capture IgM ELISAs were established with nucleocapsid proteins expressed in Drosophila melanogaster Schneider S2 cells. The cutoff values of the ELISAs were determined by investigation of up to 500 human anti-hantavirus-negative serum samples. The specificities of the Puumala and Dobrava virus-specific IgM, IgA, and IgG ELISAs were found to be 100%. The sensitivities of these ELISAs were determined to be 100% with panels of characterized anti-Puumala or anti-Dobrava virus-positive human serum samples. In most cases, Puumala and Dobrava virus infections could be differentiated by ELISA reactivity alone, i.e., endpoint titration with homologous and heterologous antigens.
Figures

References
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T. S., S. Y. Xiao, R. Stojanovic, A. Gligic, G. van der Groen, and J. W. LeDuc. 1992. Characterization of Dobrava virus: a hantavirus from Slovenia, Yugoslavia. J. Med. Virol. 38:132-137. - PubMed
-
- Avsic-Zupanc, T., M. Petrovec, P. Furlan, R. Kaps, F. Elgh, and Å. Lundkvist. 1999. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in the Dolenjska region of Slovenia—a 10-year survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28:860-865. - PubMed
-
- Biel, S. S., O. D. Mantke, K. Lemmer, A. Vaheri, A. Lundkvist, P. Emmerich, M. Hukic, and M. Niedrig. 2003. Quality control measures for the serological diagnosis of hantavirus infections. J. Clin. Virol. 28:248-256. - PubMed
-
- Billecocq, A., D. Coudrier, F. Boue, B. Combes, H. Zeller, M. Artois, and M. Bouloy. 2003. Expression of the nucleoprotein of the Puumala virus from the recombinant Semliki Forest virus replicon: characterization and use as a potential diagnostic tool. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 10:658-663. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

