Exosomal Fetuin-A identified by proteomics: a novel urinary biomarker for detecting acute kidney injury
- PMID: 17021608
- PMCID: PMC2277342
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001874
Exosomal Fetuin-A identified by proteomics: a novel urinary biomarker for detecting acute kidney injury
Abstract
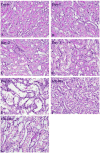
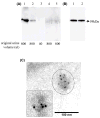
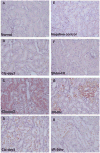
Urinary exosomes containing apical membrane and intracellular fluid are normally secreted into the urine from all nephron segments, and may carry protein markers of renal dysfunction and structural injury. We aimed to discover biomarkers in urinary exosomes to detect acute kidney injury (AKI), which has a high mortality and morbidity. Animals were injected with cisplatin. Urinary exosomes were isolated by differential centrifugation. Protein changes were evaluated by two-dimensional difference in gel electrophoresis and changed proteins were identified by mass spectrometry. The identified candidate biomarkers were validated by Western blotting in individual urine samples from rats subjected to cisplatin injection; bilateral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R); volume depletion; and intensive care unit (ICU) patients with and without AKI. We identified 18 proteins that were increased and nine proteins that were decreased 8 h after cisplatin injection. Most of the candidates could not be validated by Western blotting. However, exosomal Fetuin-A increased 52.5-fold at day 2 (1 day before serum creatinine increase and tubule damage) and remained elevated 51.5-fold at day 5 (peak renal injury) after cisplatin injection. By immunoelectron microscopy and elution studies, Fetuin-A was located inside urinary exosomes. Urinary Fetuin-A was increased 31.6-fold in the early phase (2-8 h) of I/R, but not in prerenal azotemia. Urinary exosomal Fetuin-A also increased in three ICU patients with AKI compared to the patients without AKI. We conclude that (1) proteomic analysis of urinary exosomes can provide biomarker candidates for the diagnosis of AKI and (2) urinary Fetuin-A might be a predictive biomarker of structural renal injury.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mild elevation of urinary biomarkers in prerenal acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2012 Nov;82(10):1114-20. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.266. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22854644
-
Characterization of urinary exosomal release of aquaporin-1 and -2 after renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):F584-F601. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00184.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29357442
-
Urinary exosomal transcription factors, a new class of biomarkers for renal disease.Kidney Int. 2008 Sep;74(5):613-21. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.206. Epub 2008 May 28. Kidney Int. 2008. PMID: 18509321 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) biomarker.Acta Med Indones. 2012 Jul;44(3):246-55. Acta Med Indones. 2012. PMID: 22983082 Review.
-
Prospects for urinary proteomics: exosomes as a source of urinary biomarkers.Nephrology (Carlton). 2005 Jun;10(3):283-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00387.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005. PMID: 15958043 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes: Toward a potential application in bladder cancer diagnosis and treatment.Smart Med. 2023 Oct 30;3(1):e20230027. doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20230027. eCollection 2024 Feb. Smart Med. 2023. PMID: 39188515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Exosomes Are Strongly Involved in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Feb 22;8:632290. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.632290. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33693030 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022 Aug;18(8):499-513. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00586-9. Epub 2022 May 31. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35641620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can urinary exosomes act as treatment response markers in prostate cancer?J Transl Med. 2009 Jan 12;7:4. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-4. J Transl Med. 2009. PMID: 19138409 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary proteomics reveals biological processes related to acute kidney injury in Bothrops atrox envenomings.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Mar 27;18(3):e0012072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012072. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38536893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1448–1460. - PubMed
-
- DuBose TD, Jr, Warnock DG, Mehta RL, et al. Acute renal failure in the 21st century: recommendations for management and outcomes assessment. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;29:793–799. - PubMed
-
- Star RA. Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998;54:1817–1831. - PubMed
-
- Star R. Design issues for clinical trials in acute renal failure. Blood Purif. 2001;19:233–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

