Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours
- PMID: 17022810
- PMCID: PMC1621079
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-41
Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours
Abstract
Background: Certain types of potassium channels (known as Eag1, KCNH1, Kv10.1) are associated with the production of tumours in patients and in animals. We have now studied the expression pattern of the Eag1 channel in a large range of normal and tumour tissues from different collections utilising molecular biological and immunohistochemical techniques.
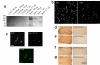
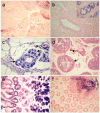
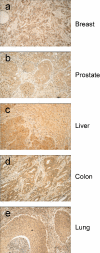
Results: The use of reverse transcription real-time PCR and specifically generated monoclonal anti-Eag1 antibodies showed that expression of the channel is normally limited to specific areas of the brain and to restricted cell populations throughout the body. Tumour samples, however, showed a significant overexpression of the channel with high frequency (up to 80% depending on the tissue source) regardless of the detection method (staining with either one of the antibodies, or detection of Eag1 RNA).
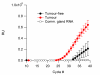
Conclusion: Inhibition of Eag1 expression in tumour cell lines reduced cell proliferation. Eag1 may therefore represent a promising target for the tailored treatment of human tumours. Furthermore, as normal cells expressing Eag1 are either protected by the blood-brain barrier or represent the terminal stage of normal differentiation, Eag1 based therapies could produce only minor side effects.
Figures


References
-
- Hille B. Ion channels of excitable membranes, Third Edition. Sunderland, Massachussets , Sinauer Associates Inc.; 2001.
-
- Conti M. Targeting K+ channels for cancer therapy. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2004;4:161–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

