Selective degradation of transcripts during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes
- PMID: 17022963
- PMCID: PMC1847322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.09.008
Selective degradation of transcripts during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes
Abstract
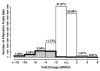
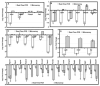
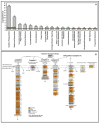
There is massive destruction of transcripts during the maturation of mouse oocytes. The objective of this project was to identify and characterize the transcripts that are degraded versus those that are stable during the transcriptionally silent germinal vesicle (GV)-stage to metaphase II (MII)-stage transition using a microarray approach. A system for oocyte transcript amplification using both internal and 3'-poly(A) priming was utilized to minimize the impact of complex variations in transcript polyadenylation prevalent during this transition. Transcripts were identified and quantified using the Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 v2.0 GeneChip. The significantly changed and stable transcripts were analyzed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis and GenMAPP/MAPPFinder to characterize the biological themes underlying global changes in oocyte transcripts during maturation. It was concluded that the destruction of transcripts during the GV to MII transition is a selective rather than promiscuous process in mouse oocytes. In general, transcripts involved in processes that are associated with meiotic arrest at the GV-stage and the progression of oocyte maturation, such as oxidative phosphorylation, energy production, and protein synthesis and metabolism, were dramatically degraded. In contrast, transcripts encoding participants in signaling pathways essential for maintaining the unique characteristics of the MII-arrested oocyte, such as those involved in protein kinase pathways, were the most prominent among the stable transcripts.
Figures


References
-
- Bachvarova R, De Leon V, Johnson A, Kaplan G, Paynton BV. Changes in total RNA, polyadenylated RNA, and actin mRNA during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Dev Biol. 1985;108:325–31. - PubMed
-
- Bettegowda A, Patel OV, Ireland JJ, Smith GW. Quantitative analysis of messenger RNA abundance for ribosomal protein L-15, cyclophilin-A, phosphoglycerokinase, beta-glucuronidase, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, beta-actin, and histone H2A during bovine oocyte maturation and early embryogenesis in vitro. Mol Reprod Dev. 2006;73:267–78. - PubMed
-
- BouniolBaly C, Hamraoui L, Guibert J, Beaujean N, Szollosi MS, Debey P. Differential transcriptional activity associated with chromatin configuration in fully grown mouse germinal vesicle oocytes. Biol Reprod. 1999;60:580–587. - PubMed
-
- Buratini J, Jr, Teixeira AB, Costa IB, Glapinski VF, Pinto MG, Giometti IC, Barros CM, Cao M, Nicola ES, Price CA. Expression of fibroblast growth factor-8 and regulation of cognate receptors, fibroblast growth factor receptor-3c and -4, in bovine antral follicles. Reproduction. 2005;130:343–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

