Peripheral quantitative computed tomography: measurement sensitivity in persons with and without spinal cord injury
- PMID: 17023249
- PMCID: PMC3272268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2006.07.257
Peripheral quantitative computed tomography: measurement sensitivity in persons with and without spinal cord injury
Abstract
Objectives: To determine (1) the error attributable to external tibia-length measurements by using peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) and (2) the effect these errors have on scan location and tibia trabecular bone mineral density (BMD) after spinal cord injury (SCI).
Design: Blinded comparison and criterion standard in matched cohorts.
Setting: Primary care university hospital.
Participants: Eight able-bodied subjects underwent tibia length measurement. A separate cohort of 7 men with SCI and 7 able-bodied age-matched male controls underwent pQCT analysis.
Interventions: Not applicable.
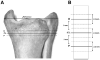
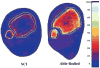
Main outcome measures: The projected worst-case tibia-length-measurement error translated into a pQCT slice placement error of +/-3 mm. We collected pQCT slices at the distal 4% tibia site, 3 mm proximal and 3 mm distal to that site, and then quantified BMD error attributable to slice placement.
Results: Absolute BMD error was greater for able-bodied than for SCI subjects (5.87 mg/cm(3) vs 4.5 mg/cm(3)). However, the percentage error in BMD was larger for SCI than able-bodied subjects (4.56% vs 2.23%).
Conclusions: During cross-sectional studies of various populations, BMD differences up to 5% may be attributable to variation in limb-length-measurement error.
Conflict of interest statement
No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit upon the author(s) or upon any organization with which the author(s) is/are associated.
Figures
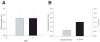
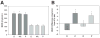
References
-
- Shields RK. Fatigability, relaxation properties, and electromyo-graphic responses of the human paralyzed soleus muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:2195–206. - PubMed
-
- Shields RK, Chang YJ. The effects of fatigue on the torque-frequency curve of the human paralysed soleus muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1997;7:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Wilmet E, Ismail AA, Heilporn A, Welraeds D, Bergmann P. Longitudinal study of the bone mineral content and of soft tissue composition after spinal cord section. Paraplegia. 1995;33:674–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

