The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III recruitment factor subunits Brf1 and Bdp1 impose a strict sequence preference for the downstream half of the TATA box
- PMID: 17028095
- PMCID: PMC1636458
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl534
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III recruitment factor subunits Brf1 and Bdp1 impose a strict sequence preference for the downstream half of the TATA box
Abstract
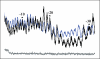
Association of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) with its cognate site within eukaryotic promoters is key to accurate and efficient transcriptional initiation. To achieve recruitment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III, TBP is associated with two additional factors, Brf1 and Bdp1, to form the initiation factor TFIIIB. Previous data have suggested that the structure or dynamics of the TBP-DNA complex may be altered upon entry of Brf1 and Bdp1 into the complex. We show here, using the altered specificity TBP mutant TBPm3 and an iterative in vitro selection assay, that entry of Brf1 and Bdp1 into the complex imposes a strict sequence preference for the downstream half of the TATA box. Notably, the selected sequence (TGTAAATA) is a perfect match to the TATA box of the RNA polymerase III-transcribed U6 small nuclear RNA (SNR6) gene. We suggest that the selected T*A base pair step at the downstream end of the 8 bp TBP site may provide a DNA flexure that promotes TFIIIB-DNA complex formation.
Figures



References
-
- Cormack B.P., Struhl K. The TATA-binding protein is required for transcription by all three nuclear RNA polymerases in yeast cells. Cell. 1992;69:685–696. - PubMed
-
- Kassavetis G.A., Braun B.R., Nguyen L.H., Geiduschek E.P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990;60:235–245. - PubMed
-
- Chaussivert N., Conesa C., Shaaban S., Sentenac A. Complex interactions between yeast TFIIIB and TFIIIC. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:15353–15358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

