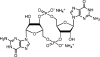
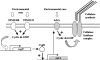
Cyclic di-GMP signaling in bacteria: recent advances and new puzzles
- PMID: 17028282
- PMCID: PMC1698238
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01079-06
Cyclic di-GMP signaling in bacteria: recent advances and new puzzles
Figures

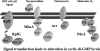
References
-
- Aldridge, P., R. Paul, P. Goymer, P. Rainey, and U. Jenal. 2003. Role of the GGDEF regulator PleD in polar development of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 47:1695-1708. - PubMed
-
- Amikam, D., and M. Y. Galperin. 2006. PilZ is part of the bacterial c-di-GMP binding protein. Bioinformatics 22:3-6. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, M. O., M. C. Alegria, C. R. Guzzo, C. Docena, M. C. P. Rosa, C. H. I. Ramos, and C. S. Farah. 2006. The HD-GYP domain of RpfG mediates a direct linkage between the Rpf quorum-sensing pathway and a subset of diguanylate cyclase proteins in the phytopathogen Xanthomonas axonopodis pv citri. Mol. Microbiol. 62:537-551. [Online.] doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05386.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ausmees, N., R. Mayer, H. Weinhouse, G. Volman, D. Amikam, M. Benziman, and M. Lindberg. 2001. Genetic data indicate that proteins containing the GGDEF domain possess diguanylate cyclase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 204:163-167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

