Application of genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism typing: simple association and beyond
- PMID: 17029559
- PMCID: PMC1592240
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020150
Application of genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism typing: simple association and beyond
Abstract
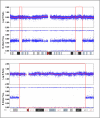
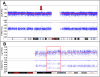
The International HapMap Project and the arrival of technologies that type more than 100,000 SNPs in a single experiment have made genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism (GW-SNP) assay a realistic endeavor. This has sparked considerable debate regarding the promise of GW-SNP typing to identify genetic association in disease. As has already been shown, this approach has the potential to localize common genetic variation underlying disease risk. The data provided from this technology also lends itself to several other lines of investigation; autozygosity mapping in consanguineous families and outbred populations, direct detection of structural variation, admixture analysis, and other population genetic approaches. In this review we will discuss the potential uses and practical application of GW-SNP typing including those above and beyond simple association testing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- The International HapMap Project. Nature. 2003;426:789–796. - PubMed
-
- Risch N, Merikangas K. The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science. 1996;273:1516–1517. - PubMed
-
- Wang WY, Barratt BJ, Clayton DG, Todd JA. Genome-wide association studies: Theoretical and practical concerns. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:109–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

