VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites
- PMID: 17032920
- PMCID: PMC1785149
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021758
VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites
Abstract
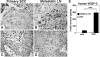
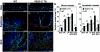
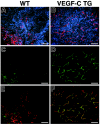
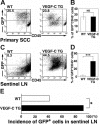
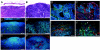
The mechanisms by which tumors metastasize to sentinel and distant lymph nodes, and beyond, are poorly understood. We developed transgenic mice that overexpress vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) and green fluorescent protein specifically in the skin and studied the effects of chemically-induced skin carcinogenesis in this model. We found that in contrast to VEGF-A, VEGF-C does not increase the growth of primary tumors, but instead induces expansion of lymphatic networks within sentinel lymph nodes, even before the onset of metastasis. Once the metastatic cells arrived at the sentinel lymph nodes, the extent of lymphangiogenesis at these sites increased. Of importance, in mice with metastasis-containing sentinel lymph nodes, tumors that expressed VEGF-C were more likely to metastasize to additional organs, such as distal lymph nodes and lungs. No metastases were observed in distant organs in the absence of lymph node metastases. These findings indicate an important role of VEGF-C-induced lymph node lymphangiogenesis in the promotion of cancer metastasis beyond the sentinel lymph nodes. VEGF-C is therefore a good target to slow or even prevent the onset of metastasis.
Figures
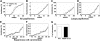
References
-
- Oliver G, Detmar M. The rediscovery of the lymphatic system: old and new insights into the development and biological function of the lymphatic vasculature. Genes Dev. 2002;16:773–783. - PubMed
-
- Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature. 2005;438:946–953. - PubMed
-
- Prevo R, Banerji S, Ferguson DJ, Clasper S, Jackson DG. Mouse LYVE-1 is an endocytic receptor for hyaluronan in lymphatic endothelium. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:19420–19430. - PubMed
-
- Wigle JT, Oliver G. Prox1 function is required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell. 1999;98:769–778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

