Role of TNFalpha in pulmonary pathophysiology
- PMID: 17034639
- PMCID: PMC1613248
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-125
Role of TNFalpha in pulmonary pathophysiology
Abstract
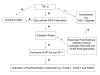
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) is the most widely studied pleiotropic cytokine of the TNF superfamily. In pathophysiological conditions, generation of TNFalpha at high levels leads to the development of inflammatory responses that are hallmarks of many diseases. Of the various pulmonary diseases, TNFalpha is implicated in asthma, chronic bronchitis (CB), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In addition to its underlying role in the inflammatory events, there is increasing evidence for involvement of TNFalpha in the cytotoxicity. Thus, pharmacological agents that can either suppress the production of TNFalpha or block its biological actions may have potential therapeutic value against a wide variety of diseases. Despite some immunological side effects, anti-TNFalpha therapeutic strategies represent an important breakthrough in the treatment of inflammatory diseases and may have a role in pulmonary diseases characterized by inflammation and cell death.
Figures

References
-
- Goto T, Ishizaka A, Kobayashi F, Kohno M, Sawafuji M, Tasaka S, Ikeda E, Okada Y, Maruyama I, Kobayashi K. Importance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha cleavage process in post-transplantation lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170:1239–1246. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200402-146OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

