Biocompatibility of septal defect closure devices
- PMID: 17035510
- PMCID: PMC1861502
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2006.098103
Biocompatibility of septal defect closure devices
Abstract
Objective: Despite their clinical introduction 10 years ago, no human series on the healing response to Amplatzer and Starflex devices in humans have been reported yet. We sought to investigate the biocompatibility of Amplatzer and Cardioseal/Starflex septal occluder devices in humans and compare the findings to results in experimental animals.
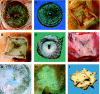
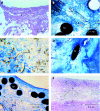
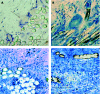
Methods: The healing response of Amplatzer and Cardioseal/Starflex septal occluder devices in humans (n = 12, follow-up periods from 5 days to 4 years) and in experimental animals (n = 32, follow-up periods from 4 days to 1 year) was studied using a uniform work up protocol. Histological sections of paraffin-wax-embedded or methacrylate-embedded specimen and scanning electron microscopy were used for biocompatibility screening.
Results: Neoendothelialisation of all examined devices was complete after 3 months in vivo. Protruding metal frame parts, like screw threads and spring arms, were covered last. The initial deposition of fibrin and blood cells on the polyester fabric was subsequently organised by ingrown fibroblastic cells. Loosely arranged and poorly vascularised young granulation tissue was transformed time-dependently into quiescent fibre-rich connective repair tissue poor of cellular and capillary vessel components. Consistently, a mild chronic inflammatory response directed against textile fibres of both types of implants characterised by lymphocytic infiltration and multinucleated foreign body giant cells was observed equally in human and animal explants.
Conclusions: Systematic biocompatibility screening in a series of explanted human septal occluder devices showed results corresponding to findings in animal studies with regard to neoendothelialisation, cellular organisation of initial thrombus and persisting immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical characterization of neotissues and tissue reactions to septal defect-occlusion devices.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009 Apr;2(2):90-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.108.810507. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009. PMID: 20031701
-
Interventional atrial septal defect closure using a totally bioresorbable occluder matrix: development and preclinical evaluation of the BioSTAR device.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Jul 4;48(1):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.02.057. Epub 2006 Jun 9. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16814662
-
A new biological matrix for septal occlusion.J Interv Cardiol. 2003 Apr;16(2):149-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8183.2003.08027.x. J Interv Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12768918
-
Biocompatibility screening in cardiovascular implants.Z Kardiol. 2005 Jun;94(6):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s00392-005-0231-4. Z Kardiol. 2005. PMID: 15940438 Review.
-
Percutaneous catheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects: a review.J Invasive Cardiol. 2002 Jan;14(1):25-31. J Invasive Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 11773692 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological variations of the interatrial septum in ovine heart.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 19;13(12):e0209604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209604. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30566482 Free PMC article.
-
Bioabsorbable atrial septal occluder for percutaneous closure of atrial septal defect in children.Tex Heart Inst J. 2012;39(2):184-9. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012. PMID: 22740729 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Occluders for Device Healing and Nickel Release in a Chronic Porcine Model.J Interv Cardiol. 2020 Jun 20;2020:8413831. doi: 10.1155/2020/8413831. eCollection 2020. J Interv Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32665769 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal septicemia in a patient with cerebral lymphoma and an Amplatzer septal occluder: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2011 Nov 24;5:554. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-554. J Med Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 22115504 Free PMC article.
-
Intermediate and long-term followup of percutaneous device closure of fossa ovalis atrial septal defect by the Amplatzer septal occluder in a cohort of 529 patients.Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2011 Jan;4(1):22-7. doi: 10.4103/0974-2069.79618. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21677800 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources