Bombesin receptors as a novel anti-anxiety therapeutic target: BB1 receptor actions on anxiety through alterations of serotonin activity
- PMID: 17035523
- PMCID: PMC6674684
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1219-06.2006
Bombesin receptors as a novel anti-anxiety therapeutic target: BB1 receptor actions on anxiety through alterations of serotonin activity
Abstract
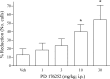
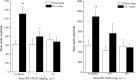
The effects of PD 176252 [3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-N-[1-(5-methoxy-pyridin-2-yl)-cyclohexylmethyl]-2-methyl-2-[3-(nitro-phenyl)ureido]propionamide], a nonpeptide bombesin (BB) BB1/BB2 receptor antagonist, were assessed in rats using several ethologically relevant tests of anxiety. Consistent with a role for the bombesin family of peptides in subserving anxiety behaviors, the antagonist increased social interaction (3.75 and 7.5 mg/kg, i.p.), dose-dependently attenuated the number of vocalizations emitted by guinea pig pups separated from their mother (1-30 mg/kg, i.p.), reduced latency to approach a palatable snack in an anxiogenic (unfamiliar) environment, and reduced the fear-potentiated startle response (5 and 10 mg/kg, i.p., and 100-200 ng per rat, i.c.v.). When administered directly to the dorsal raphé nucleus (DRN), PD 176252 (20-500 ng) increased social interaction under aversive conditions, as did the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (50 ng). Furthermore, intra-DRN microinfusion of the peptide antagonist (PD 176252) suppressed, whereas its agonist [neuromedin B (NMB)-30] promoted, the in vivo release of 5-HT in the ventral hippocampus. In parallel, the suppressed social interaction elicited by intra-DRN administration of NMB was attenuated by a systemically administered 5-HT2C (but not 5-HT1A) receptor antagonist. Together, these findings suggest that endogenous BB-like peptides at the DRN evoke the release of 5-HT from the limbic nerve terminals originating from the raphé, specifically at the ventral hippocampus, resulting in anxiogenesis. The finding that this action was attenuated by BB receptor (BB1 and/or BB2) antagonists suggests that these compounds may represent a novel class of anxiolytic agents.
Figures





References
-
- Alves SH, Pinheiro G, Motta V, Landeira-Fernandez J. Anxiogenic effects in the rat elevated plus-maze of 5-HT(2C) agonists into the ventral but not the dorsal hippocampus. Behav Pharmacol. 2004;15:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Andrews N, Hogg S, Gonzalez LE, File SE. 5-HT1A receptors in the median raphe nucleus and dorsal hippocampus may mediate anxiolytic and anxiogenic behaviours respectively. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;264:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Anismam H, Matheson K. Stress, depression, and anhedonia: caveats concerning animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29:525–546. - PubMed
-
- Ashwood V, Brownhill V, Higginbottom M, Horwell DC, Hughes J, Lewthwaite RA, McKnight AT, Pinnock RD, Pritchard MC, Suman-Chauhan N, Webb C, Williams SC. PD 176252–the first high affinity non-peptide gastrin-releasing peptide (BB2) receptor antagonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998;8:2589–2594. - PubMed
-
- Battey J, Wada E. Two distinct receptor subtypes for mammalian bombesin-like peptides. Trends Neurosci. 1991;14:524–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
