Help-seeking pathways in early psychosis
- PMID: 17036265
- PMCID: PMC1764202
- DOI: 10.1007/s00127-006-0117-4
Help-seeking pathways in early psychosis
Abstract
Introduction: Understanding the help-seeking pathways of patients with a putative risk of developing psychosis helps improving development of specialised care services. This study aimed at obtaining information about: type of health professionals contacted by patients at putative risk for psychosis on their help-seeking pathways; number of contacts; type of symptoms leading to contacts with health professionals; interval between initial contact and referral to a specialised outpatient service.
Method: The help-seeking pathways were assessed as part of a prospective study in 104 patients with suspected at-risk states for psychosis.
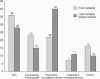
Results: The mean number of contacts prior to referral was 2.38. Patients with psychotic symptoms more often contacted mental health professionals, whereas patients with insidious and more unspecific features more frequently contacted general practitioners (GPs).
Conclusions: GPs have been found to under-identify the insidious features of emerging psychosis (Simon et al. (2005) Br J Psychiatry 187:274-281). The fact that they were most often contacted by patients with exactly these features calls for focussed and specialised help for primary care physicians. Thus, delays along the help-seeking pathways may be shortened. This may be of particular relevance for patients with the deficit syndrome of schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1046/j.1440-1614.1999.00613.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1614.1999.00613.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10619220', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10619220/'}]}
- Phillips L, Yung AR, Hearn N, McFarlane C, Hallgren M, McGorry PD (1999) Preventive mental health care: accessing the target population. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 33:912–917 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3697578', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3697578/'}]}
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Johnson AL, MacMillan JF (1986) The Northwick Park Study of first episodes of schizophrenia. I. Presentation of the illness and problems relating to admission. Br J Psychiatry 148:115–120 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9764122', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9764122/'}]}
- Lincoln CV, Harrigan S, McGorry PD (1998) Understanding the topography of the early psychosis pathways. Br J Psychiatry 172(suppl.33):21–25 - PubMed
-
- Skeate A, Jackson C, Birchwood M, Jones C (2002) Duration of untreated psychosis and pathways to care in first-episode psychosis. Investigation of help-seeking behaviour in primary care. Br J Psychiatry (Suppl. 43):73–77 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.02004.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.02004.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12366470', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12366470/'}]}
- Addington J, Van Mastrigt S, Hutchinson J, Addington D (2002) Pathways to care: help seeking behaviour in first episode psychosis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 106:358–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical