Flexibility and constraint in the nucleosome core landscape of Caenorhabditis elegans chromatin
- PMID: 17038564
- PMCID: PMC1665634
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.5560806
Flexibility and constraint in the nucleosome core landscape of Caenorhabditis elegans chromatin
Abstract
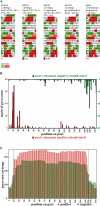
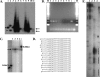
Nucleosome positions within the chromatin landscape are known to serve as a major determinant of DNA accessibility to transcription factors and other interacting components. To delineate nucleosomal patterns in a model genetic organism, Caenorhabditis elegans, we have carried out a genome-wide analysis in which DNA fragments corresponding to nucleosome cores were liberated using an enzyme (micrococcal nuclease) with a strong preference for cleavage in non-nucleosomal regions. Sequence analysis of 284,091 putative nucleosome cores obtained in this manner from a mixed-stage population of C. elegans reveals a combined picture of flexibility and constraint in nucleosome positioning. As has previously been observed in studies of individual loci in diverse biological systems, we observe areas in the genome where nucleosomes can adopt a wide variety of positions in a given region, areas with little or no nucleosome coverage, and areas where nucleosomes reproducibly adopt a specific positional pattern. In addition to illuminating numerous aspects of chromatin structure for C. elegans, this analysis provides a reference from which to begin an investigation of relationships between the nucleosomal pattern, chromosomal architecture, and lineage-based gene activity on a genome-wide scale.
Figures
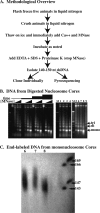
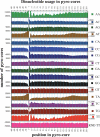

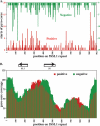
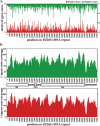
References
-
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975;14:2921–2925. - PubMed
-
- Baer B.W., Kornberg R.D., Kornberg R.D. Random location of nucleosomes on genes for 5 S rRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1979;254:9678–9681. - PubMed
-
- Brower-Toland B.D., Smith C.L., Yeh R.C., Lis J.T., Peterson C.L., Wang M.D., Smith C.L., Yeh R.C., Lis J.T., Peterson C.L., Wang M.D., Yeh R.C., Lis J.T., Peterson C.L., Wang M.D., Lis J.T., Peterson C.L., Wang M.D., Peterson C.L., Wang M.D., Wang M.D. Mechanical disruption of individual nucleosomes reveals a reversible multistage release of DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002;99:1960–1965. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buttinelli M., Panetta G., Rhodes D., Travers A., Panetta G., Rhodes D., Travers A., Rhodes D., Travers A., Travers A. The role of histone H1 in chromatin condensation and transcriptional repression. Genetica. 1999;106:117–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
