Enhanced yield of neuroepithelial precursors and midbrain-like dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells using the bone morphogenic protein antagonist noggin
- PMID: 17038668
- PMCID: PMC2667240
- DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0380
Enhanced yield of neuroepithelial precursors and midbrain-like dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells using the bone morphogenic protein antagonist noggin
Abstract
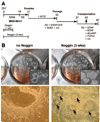
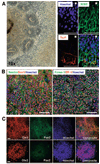
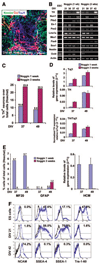
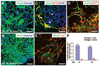
It is currently not known whether dopamine (DA) neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) can survive in vivo and alleviate symptoms in models of Parkinson disease (PD). Here, we report the use of Noggin (a bone morphogenic protein antagonist) to induce neuroectodermal cell development and increase the yield of DA neurons from hESCs. A combination of stromal-derived inducing activity and Noggin markedly enhanced the generation of neuroepithelial progenitors that could give rise to DA neurons. In addition, Noggin diminished the occurrence of a fibroblast-like Nestin-positive precursor population that differentiated into myocytes. After transplantation of differentiated hESCs to a rodent model of PD, some grafts contained human midbrain-like DA neurons. This protocol demonstrates hESC derivation and survival of human DA neurons appropriate for cell therapy in PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zeng X, Cai J, Chen J, et al. Dopaminergic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. STEM CELLS. 2004;22:925–940. - PubMed
-
- Buytaert-Hoefen KA, Alvarez E, Freed CR. Generation of tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons from human embryonic stem cells after coculture with cellular substrates and exposure to GDNF. STEM CELLS. 2004;22:669–674. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Hur T, Idelson M, Khaner H, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors improves behavioral deficit in Parkinsonian rats. STEM CELLS. 2004;22:1246–1255. - PubMed
-
- Park CH, Minn YK, Lee JY, et al. In vitro and in vivo analyses of human embryonic stem cell-derived dopamine neurons. J Neurochem. 2005;92:1265–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

