Bundle-branch block with short P-R interval in healthy young people prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. 1930
- PMID: 17040283
- PMCID: PMC6932258
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2006.00127.x
Bundle-branch block with short P-R interval in healthy young people prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. 1930
Figures
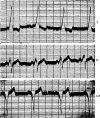
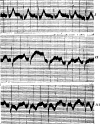
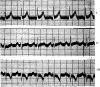
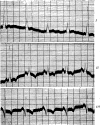







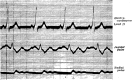
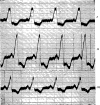

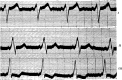
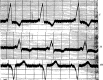
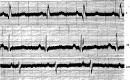

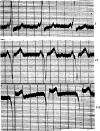

References
-
- Carter, E. P .: Clinical Observations on Defective Conduction in the Branches of the Auriculo‐Ventricular Bundle. Arch. Int. Med., 13, 803, 1914.
-
- Cohn, A. E. , and Lewis, T .: The Pathology of Bundle‐Branch Lesions of the Heart. Proc. N. Y. Path. Soc., 14, 207, 1914.
-
- Eppinger, H. , Und Rothberger, J .: Zur Analyse des Elektrokardiogramms. Wien Klin. Wchnschr., 22, 1091,1909.
-
- Eppinger, H. , Und Rothberger, J .: Ueber die Folgen der Durchschneidung der Tawaraschen Schenkel des Reizleitungssystems. Ztschr. f. klin. Med., 70, 1, 1910.
-
- Eppinger, H. , Und Stoerk, O. : Zur Klinik des Elektrokardiogramms. Ztschr. f. klin. Med., 71, 157, 1910.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Personal name as subject
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

