Dynamic response of prevacuolar compartments to brefeldin a in plant cells
- PMID: 17041023
- PMCID: PMC1676059
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.090423
Dynamic response of prevacuolar compartments to brefeldin a in plant cells
Abstract
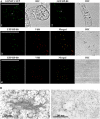
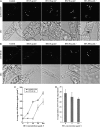
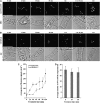
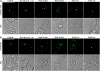
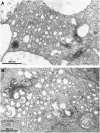
Little is known about the dynamics and molecular components of plant prevacuolar compartments (PVCs) in the secretory pathway. Using transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Bright-Yellow-2 (BY-2) cells expressing membrane-anchored yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) reporters marking Golgi or PVCs, we have recently demonstrated that PVCs are mobile multivesicular bodies defined by vacuolar sorting receptor proteins. Here, we demonstrate that Golgi and PVCs have different sensitivity in response to brefeldin A (BFA) treatment in living tobacco BY-2 cells. BFA at low concentrations (5-10 microg mL(-1)) induced YFP-marked Golgi stacks to form both endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi hybrid structures and BFA-induced aggregates, but had little effect on YFP-marked PVCs in transgenic BY-2 cells at both confocal and immunogold electron microscopy levels. However, BFA at high concentrations (50-100 microg mL(-1)) caused both YFP-marked Golgi stacks and PVCs to form aggregates in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Normal Golgi or PVC signals can be recovered upon removal of BFA from the culture media. Confocal immunofluorescence and immunogold electron microscopy studies with specific organelle markers further demonstrate that the PVC aggregates are distinct, but physically associated, with Golgi aggregates in BFA-treated cells and that PVCs might lose their internal vesicle structures at high BFA concentration. In addition, vacuolar sorting receptor-marked PVCs in root-tip cells of tobacco, pea (Pisum sativum), mung bean (Vigna radiata), and Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) upon BFA treatment are also induced to form similar aggregates. Thus, we have demonstrated that the effects of BFA are not limited to endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, but extend to PVC in the endomembrane system, which might provide a quick tool for distinguishing Golgi from PVC for its identification and characterization, as well as a possible new tool in studying PVC-mediated protein traffic in plant cells.
Figures
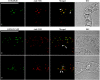
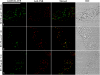
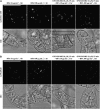
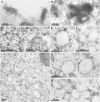
References
-
- Bethke PC, Jones RL (2000) Vacuoles and prevacuolar compartments. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3: 469–475 - PubMed
-
- Boevink P, Oparka K, Santa CS, Martin B, Betteridge A, Hawes C (1998) Stacks on tracks: the plant Golgi apparatus traffics on an actin/ER network. Plant J 15: 441–447 - PubMed
-
- Bright NA, Lindsay MR, Stewart A, Luzio JP (2001) The relationship between lumenal and limiting membranes in swollen late endocytic compartments formed after wortmannin treatment or sucrose accumulation. Traffic 2: 631–642 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

