Analysis of the roles of FlgP and FlgQ in flagellar motility of Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 17041040
- PMCID: PMC1797208
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01199-06
Analysis of the roles of FlgP and FlgQ in flagellar motility of Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
Flagellar motility is an important determinant of Campylobacter jejuni that is required for promoting interactions with various hosts to promote gastroenteritis in humans or commensal colonization of many animals. In a previous study, we identified a nonmotile mutant of C. jejuni 81-176 with a transposon insertion in Cj1026c, but verification of the role of the encoded protein in motility was not determined. In this study, we have determined that Cj1026c and the gene immediately downstream, Cj1025c (here annotated as flgP and flgQ, respectively), are both required for motility of C. jejuni but not for flagellar biosynthesis. FlgP and FlgQ are not components of the transcriptional regulatory cascades to activate sigma(28)- or sigma(54)-dependent expression of flagellar genes. In addition, expression of flgP and flgQ is not largely dependent on sigma(28) or sigma(54). Immunblot analyses revealed that the majority of FlgP in C. jejuni is associated with the outer membrane. However, in the absence of FlgQ, the amounts of FlgP in the outer membrane of C. jejuni are greatly reduced, suggesting that FlgQ may be required for localization or stability of FlgP at this location. This study provides insight into features of FlgP and FlgQ, two proteins with previously undefined functions that are required for the larger, multicomponent flagellar system of C. jejuni that is necessary for motility.
Figures
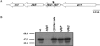


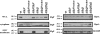
Similar articles
-
Role of motAB in adherence and internalization in polarized Caco-2 cells and in cecal colonization of Campylobacter jejuni.Avian Dis. 2013 Mar;57(1):116-22. doi: 10.1637/10235-050412-ResNote.1. Avian Dis. 2013. PMID: 23678739
-
Characterization of two outer membrane proteins, FlgO and FlgP, that influence vibrio cholerae motility.J Bacteriol. 2009 Sep;191(18):5669-79. doi: 10.1128/JB.00632-09. Epub 2009 Jul 10. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19592588 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the Campylobacter jejuni FlgSR two-component system is linked to the flagellar export apparatus.J Bacteriol. 2009 Apr;191(8):2656-67. doi: 10.1128/JB.01689-08. Epub 2009 Feb 6. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19201799 Free PMC article.
-
Motility and chemotaxis in Campylobacter and Helicobacter.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2011;65:389-410. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-090110-102908. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21939377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Campylobacter jejuni transducer like proteins: Chemotaxis and beyond.Gut Microbes. 2017 Jul 4;8(4):323-334. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1279380. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Gut Microbes. 2017. PMID: 28080213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversification of Campylobacter jejuni Flagellar C-Ring Composition Impacts Its Structure and Function in Motility, Flagellar Assembly, and Cellular Processes.mBio. 2020 Jan 7;11(1):e02286-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02286-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31911488 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular model of a bacterial flagellar motor in situ reveals a "parts-list" of protein adaptations to increase torque.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 9:2023.09.08.556779. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.08.556779. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Microbiol. 2025 Jul;10(7):1723-1740. doi: 10.1038/s41564-025-02012-9. PMID: 39416179 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Viscosity-dependent determinants of Campylobacter jejuni impacting the velocity of flagellar motility.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0254423. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02544-23. Epub 2023 Dec 12. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38085029 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of FlgP, an Essential Protein for Flagellar Assembly in Rhodobacter sphaeroides.J Bacteriol. 2019 Feb 11;201(5):e00752-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00752-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30559113 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter coli Prosthetic Joint Infection: Case Report and a Review of the Literature.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 27;13(10):838. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100838. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alm, R. A., L. S. Ling, D. T. Moir, B. L. King, E. D. Brown, P. C. Doig, D. R. Smith, B. Noonan, B. C. Guild, B. L. deJonge, G. Carmel, P. J. Tummino, A. Caruso, M. Uria-Nickelsen, D. M. Mills, C. Ives, R. Gibson, D. Merberg, S. D. Mills, Q. Jiang, D. E. Taylor, G. F. Vovis, and T. J. Trust. 1999. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397:176-180. - PubMed
-
- Baar, C., M. Eppinger, G. Raddatz, J. Simon, C. Lanz, O. Klimmek, R. Nandakumar, R. Gross, A. Rosinus, H. Keller, P. Jagtap, B. Linke, F. Meyer, H. Lederer, and S. C. Schuster. 2003. Complete genome sequence and analysis of Wolinella succinogenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:11690-11695. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black, R. E., M. M. Levine, M. L. Clements, T. P. Hughes, and M. J. Blaser. 1988. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect. Dis. 157:472-479. - PubMed
-
- Blair, D. F. 2003. Flagellar movement driven by proton translocation. FEBS Lett. 545:86-95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

