N-acetylanthranilate amidase from Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a, an alpha/beta-hydrolase-fold protein active towards aryl-acylamides and -esters, and properties of its cysteine-deficient variant
- PMID: 17041061
- PMCID: PMC1698245
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01085-06
N-acetylanthranilate amidase from Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a, an alpha/beta-hydrolase-fold protein active towards aryl-acylamides and -esters, and properties of its cysteine-deficient variant
Erratum in
- J Bacteriol. 2007 May;189(10):3933
Abstract
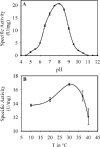
N-acetylanthranilate amidase (Amq), a 32.8-kDa monomeric amide hydrolase, is involved in quinaldine degradation by Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a. Sequence analysis and secondary structure predictions indicated that Amq is related to carboxylesterases and belongs to the alpha/beta-hydrolase-fold superfamily of enzymes; inactivation of (His(6)-tagged) Amq by phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride and diethyl pyrocarbonate and replacement of conserved residues suggested a catalytic triad consisting of S155, E235, and H266. Amq is most active towards aryl-acetylamides and aryl-acetylesters. Remarkably, its preference for ring-substituted analogues was different for amides and esters. Among the esters tested, phenylacetate was hydrolyzed with highest catalytic efficiency (k(cat)/K(m) = 208 mM(-1) s(-1)), while among the aryl-acetylamides, o-carboxy- or o-nitro-substituted analogues were preferred over p-substituted or unsubstituted compounds. Hydrolysis by His(6)Amq of primary amides, lactams, N-acetylated amino acids, azocoll, tributyrin, and the acylanilide and urethane pesticides propachlor, propham, carbaryl, and isocarb was not observed; propanil was hydrolyzed with 1% N-acetylanthranilate amidase activity. The catalytic properties of the cysteine-deficient variant His(6)AmqC22A/C63A markedly differed from those of His(6)Amq. The replacements effected some changes in K(m)s of the enzyme and increased k(cat)s for most aryl-acetylesters and some aryl-acetylamides by factors of about three to eight while decreasing k(cat) for the formyl analogue N-formylanthranilate by several orders of magnitude. Circular dichroism studies indicated that the cysteine-to-alanine replacements resulted in significant change of the overall fold, especially an increase in alpha-helicity of the cysteine-deficient protein. The conformational changes may also affect the active site and may account for the observed changes in kinetic properties.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of large linear plasmids in Arthrobacter spp. encoding the degradation of quinaldine to anthranilate.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Feb;151(Pt 2):491-500. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27521-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15699198
-
Mandelamide hydrolase from Pseudomonas putida: characterization of a new member of the amidase signature family.Biochemistry. 2004 Jun 22;43(24):7725-35. doi: 10.1021/bi049907q. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15196015
-
EstA from Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a, a thermo- and solvent-tolerant carboxylesterase related to class C beta-lactamases.Curr Microbiol. 2007 Mar;54(3):230-6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-006-0438-2. Curr Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17294326
-
Scope, limitations and classification of lactamases.J Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 10;235:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.03.050. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27046068 Review.
-
Amidase domains from bacterial and phage autolysins define a family of gamma-D,L-glutamate-specific amidohydrolases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 May;28(5):230-4. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(03)00062-8. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003. PMID: 12765833 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico screening of 393 mutants facilitates enzyme engineering of amidase activity in CalB.PeerJ. 2013 Aug 29;1:e145. doi: 10.7717/peerj.145. eCollection 2013. PeerJ. 2013. PMID: 24010022 Free PMC article.
-
The PaaX-type repressor MeqR2 of Arthrobacter sp. strain Rue61a, involved in the regulation of quinaldine catabolism, binds to its own promoter and to catabolic promoters and specifically responds to anthraniloyl coenzyme A.J Bacteriol. 2013 Mar;195(5):1068-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.01547-12. Epub 2012 Dec 28. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23275246 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning of a novel arylamidase gene from Paracoccus sp. strain FLN-7 that hydrolyzes amide pesticides.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jul;78(14):4848-55. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00320-12. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22544249 Free PMC article.
-
Subtilase from Beauveria sp.: conformational and functional investigation of unusual stability.Eur Biophys J. 2014 Sep;43(8-9):393-403. doi: 10.1007/s00249-014-0971-z. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Eur Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24925574
-
Characterization of a novel amidohydrolase with promiscuous esterase activity from a soil metagenomic library and its application in degradation of amide herbicides.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(14):20970-20982. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32362-6. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38383926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aboulmagd, E., F. B. Oppermann-Sanio, and A. Steinbüchel. 2000. Molecular characterization of the cyanophycin synthetase from Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6308. Arch. Microbiol. 174:297-306. - PubMed
-
- Aiyar, A. 2000. The use of CLUSTAL W and CLUSTAL X for multiple sequence alignment. Methods Mol. Biol. 132:221-241. - PubMed
-
- Akutsu-Shigeno, Y., Y. Adachi, C. Yamada, K. Toyoshima, N. Nomura, H. Uchiyama, and T. Nakajima-Kambe. 2006. Isolation of a bacterium that degrades urethane compounds and characterization of its urethane hydrolase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 70:422-429. - PubMed
-
- Alam, M., D. E. Vance, and R. Lehner. 2002. Structure-function analysis of human triacylglycerol hydrolase by site-directed mutagenesis: identification of the catalytic triad and a glycosylation site. Biochemistry 41:6679-6687. - PubMed
-
- Allebrandt, K. V., V. Rajesh, and P. G. Layer. 2005. Expression of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and aryl acylamidase (AAA) during early zebrafish embryogenesis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 157-158:353-355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

