Binding specificities and potential roles of isoforms of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in Leishmania
- PMID: 17041189
- PMCID: PMC1694823
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00230-06
Binding specificities and potential roles of isoforms of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in Leishmania
Abstract
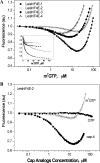
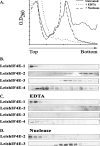
The 5' cap structure of trypanosomatid mRNAs, denoted cap 4, is a complex structure that contains unusual modifications on the first four nucleotides. We examined the four eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) homologues found in the Leishmania genome database. These proteins, denoted LeishIF4E-1 to LeishIF4E-4, are located in the cytoplasm. They show only a limited degree of sequence homology with known eIF4E isoforms and among themselves. However, computerized structure prediction suggests that the cap-binding pocket is conserved in each of the homologues, as confirmed by binding assays to m(7)GTP, cap 4, and its intermediates. LeishIF4E-1 and LeishIF4E-4 each bind m(7)GTP and cap 4 comparably well, and only these two proteins could interact with the mammalian eIF4E binding protein 4EBP1, though with different efficiencies. 4EBP1 is a translation repressor that competes with eIF4G for the same residues on eIF4E; thus, LeishIF4E-1 and LeishIF4E-4 are reasonable candidates for serving as translation factors. LeishIF4E-1 is more abundant in amastigotes and also contains a typical 3' untranslated region element that is found in amastigote-specific genes. LeishIF4E-2 bound mainly to cap 4 and comigrated with polysomal fractions on sucrose gradients. Since the consensus eIF4E is usually found in 48S complexes, LeishIF4E-2 could possibly be associated with the stabilization of trypanosomatid polysomes. LeishIF4E-3 bound mainly m(7)GTP, excluding its involvement in the translation of cap 4-protected mRNAs. It comigrates with 80S complexes which are resistant to micrococcal nuclease, but its function is yet unknown. None of the isoforms can functionally complement the Saccharomyces cerevisiae eIF4E, indicating that despite their structural conservation, they are considerably diverged.
Figures





References
-
- Altmann, M., I. Edery, H. Trachsel, and N. Sonenberg. 1988. Site-directed mutagenesis of the tryptophan residues in yeast eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Effects on cap binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 263:17229-17232. - PubMed
-
- Altmann, M., P. P. Muller, J. Pelletier, N. Sonenberg, and H. Trachsel. 1989. A mammalian translation initiation factor can substitute for its yeast homologue in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 264:12145-12147. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, J., and G. W. Zieve. 1991. Assembly and intracellular transport of snRNP particles. Bioessays 13:57-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

