The activity and stability of the transcriptional coactivator p/CIP/SRC-3 are regulated by CARM1-dependent methylation
- PMID: 17043108
- PMCID: PMC1800659
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00815-06
The activity and stability of the transcriptional coactivator p/CIP/SRC-3 are regulated by CARM1-dependent methylation
Abstract
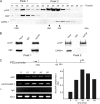
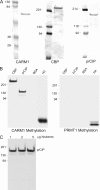
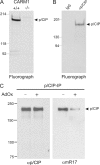
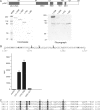
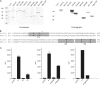
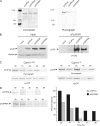
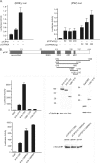
The transcriptional coactivator p/CIP(SRC-3/AIB1/ACTR/RAC3) binds liganded nuclear hormone receptors and facilitates transcription by directly recruiting accessory factors such as acetyltransferase CBP/p300 and the coactivator arginine methyltransferase CARM1. In the present study, we have established that recombinant p/CIP (p300/CBP interacting protein) is robustly methylated by CARM1 in vitro but not by other protein arginine methyltransferase family members. Metabolic labeling of MCF-7 breast cancer cells with S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-(3)H]methionine and immunoblotting using dimethyl arginine-specific antibodies demonstrated that p/CIP is specifically methylated in intact cells. In addition, methylation of full-length p/CIP is not supported by extracts derived from CARM1(-/-) mouse embryo fibroblasts, indicating that CARM1 is required for p/CIP methylation. Using mass spectrometry, we have identified three CARM1-dependent methylation sites located in a glutamine-rich region within the carboxy terminus of p/CIP which are conserved among all steroid receptor coactivator proteins. These results were confirmed by in vitro methylation of p/CIP using carboxy-terminal truncation mutants and synthetic peptides as substrates for CARM1. Analysis of methylation site mutants revealed that arginine methylation causes an increase in full-length p/CIP turnover as a result of enhanced degradation. Additionally, methylation negatively impacts transcription via a second mechanism by impairing the ability of p/CIP to associate with CBP. Collectively, our data highlight coactivator methylation as an important regulatory mechanism in hormonal signaling.
Figures
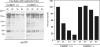
Similar articles
-
Synergistic, p160 coactivator-dependent enhancement of estrogen receptor function by CARM1 and p300.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):40810-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005459200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11010967
-
Signaling within a coactivator complex: methylation of SRC-3/AIB1 is a molecular switch for complex disassembly.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):7846-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00568-06. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16923966 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase.Science. 1999 Jun 25;284(5423):2174-7. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5423.2174. Science. 1999. PMID: 10381882
-
Review of the in vivo functions of the p160 steroid receptor coactivator family.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 Sep;17(9):1681-92. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0116. Epub 2003 Jun 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12805412 Review.
-
The roles of protein-protein interactions and protein methylation in transcriptional activation by nuclear receptors and their coactivators.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;85(2-5):139-45. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00222-x. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12943698 Review.
Cited by
-
Minireview: nuclear receptor coregulators of the p160 family: insights into inflammation and metabolism.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;29(4):502-17. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1005. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25647480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein arginine methylation/demethylation and cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 11;7(41):67532-67550. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11376. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CARM1 promotes adipocyte differentiation by coactivating PPARgamma.EMBO Rep. 2008 Feb;9(2):193-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401151. Epub 2008 Jan 11. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18188184 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating Anopheles gambiae coactivator associated arginine methyltransferase 1 automethylation using top-down high resolution tandem mass spectrometry.Protein Sci. 2009 Jun;18(6):1272-80. doi: 10.1002/pro.139. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19472346 Free PMC article.
-
CARM1 hypermethylates the NuRD chromatin remodeling complex to promote cell cycle gene expression and breast cancer development.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 8;52(12):6811-6829. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae329. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38676947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anafi, M., Y. F. Yang, N. A. Barlev, M. V. Govindan, S. L. Berger, T. R. Butt, and P. G. Walfish. 2000. GCN5 and ADA adaptor proteins regulate triiodothyronine/GRIP1 and SRC-1 coactivator-dependent gene activation by the human thyroid hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 14:718-732. - PubMed
-
- Anzick, S. L., J. Kononen, R. L. Walker, D. O. Azorsa, M. M. Tanner, X. Y. Guan, G. Sauter, O. P. Kallioniemi, J. M. Trent, and P. S. Meltzer. 1997. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277:965-968. - PubMed
-
- Bedford, M. T., and S. Richard. 2005. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol. Cell 18:263-272. - PubMed
-
- Beischlag, T. V., S. Wang, D. W. Rose, J. Torchia, S. Reisz-Porszasz, K. Muhammad, W. E. Nelson, M. R. Probst, M. G. Rosenfeld, and O. Hankinson. 2002. Recruitment of the NCoA/SRC-1/p160 family of transcriptional coactivators by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:4319-4333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown, K., Y. Chen, T. M. Underhill, J. S. Mymyrk, and J. Torchia. 2003. The coactivator p/CIP/SRC-3 facilitates retinoic acid receptor signalling via recruitment of GCN5. J. Biol. Chem. 278:39402-39412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
