Combination of multiplex PCRs for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type assignment: rapid identification system for mec, ccr, and major differences in junkyard regions
- PMID: 17043114
- PMCID: PMC1797693
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00165-06
Combination of multiplex PCRs for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type assignment: rapid identification system for mec, ccr, and major differences in junkyard regions
Abstract
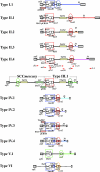
Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) typing, in combination with genotyping of the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome, has become essential for defining methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) clones in epidemiological studies. We have developed a convenient system for SCCmec type assignment. The system consists of six multiplex PCRs (M-PCRs) for identifying the ccr gene complex (ccr), the mec gene complex (mec), and specific structures in the junkyard (J) regions: M-PCR with primer set 1 (M-PCR 1) identified five types of ccr genes; M-PCR 2 identified class A to class C mec; M-PCRs 3 and 4 identified specific open reading frames in the J1 regions of type I and IV and of type II, III, and V SCCmec elements, respectively; M-PCR 5 identified the transposons Tn554 and PsiTn554 integrated into the J2 regions of type II and III SCCmec elements; and M-PCR 6 identified plasmids pT181 and pUB110 integrated into J3 regions. The system was validated with 99 MRSA strains carrying SCCmec elements of different types. The SCCmec types of 93 out of the 99 MRSA strains could be assigned. The SCCmec type assignments were identical to those made with a PCR system that uses numerous primer pairs to identify genes or gene alleles. Our system of six M-PCRs is thus a convenient and reliable method for typing SCCmec elements.
Figures

References
-
- Cha, H. Y., D. C. Moon, C. H. Choi, J. Y. Oh, Y. S. Jeong, Y. C. Lee, S. Y. Seol, D. T. Cho, H. H. Chang, S. W. Kim, and J. C. Lee. 2005. Prevalence of the ST239 clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and differences in antimicrobial susceptibilities of ST239 and ST5 clones identified in a Korean hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:3610-3614. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chongtrakool, P., T. Ito, X. X. Ma, Y. Kondo, S. Trakulsomboon, C. Tiensasitorn M. Jamklang, T. Chavalit, J.-H. Song, and K. Hiramatsu. 2006. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) typing of MRSA strains isolated in 11 Asian countries: a proposal for a new nomenclature for SCCmec elements. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1001-1012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deresinski, S. 2005. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an evolutionary, epidemiologic, and therapeutic odyssey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40:562-573. - PubMed
-
- Eady, E. A., and J. H. Cove. 2003. Staphylococcal resistance revisited: community-acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus—an emerging problem for the management of skin and soft tissue infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 16:103-124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

