An inherent role of microtubule network in the action of nuclear receptor
- PMID: 17043237
- PMCID: PMC1635113
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607445103
An inherent role of microtubule network in the action of nuclear receptor
Abstract
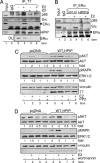
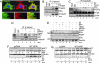
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) functions as both a transcription factor and a mediator of rapid estrogen signaling. Recent studies have shown a role for ERalpha-interacting membranous and cytosolic proteins in ERalpha action, but our understanding of the role of the microtubule network in the modulation of ERalpha signaling remains unclear. Here we found that endogenous ERalpha associates with microtubules through the microtubule-binding protein hematopoietic PBX-interaction protein (HPIP). Biochemical and RNA-interference studies demonstrated that HPIP influences ERalpha-dependent rapid estrogen signaling by acting as a scaffold protein and recruits Src kinase and the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to a complex with ERalpha, which in turn stimulates AKT and MAPK. We also found that ERalpha interacts with beta-tubulin through HPIP. Destabilization of microtubules activated ERalpha signaling, whereas stabilization of microtubules repressed ERalpha transcriptional activity in a HPIP-dependent manner. These findings revealed a role for HPIP-microtubule complex in regulating 17beta-estradiol-ERalpha responses in mammalian cells and discovered an inherent role of microtubules in the action of nuclear receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The estrogen receptor-interacting protein HPIP increases estrogen-responsive gene expression through activation of MAPK and AKT.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jun;1783(6):1220-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.026. Epub 2008 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18302941
-
Phosphorylation of MNAR promotes estrogen activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(5):1904-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01732-06. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. Retraction in: Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Mar;30(6):1568. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00090-10. PMID: 17194752 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Estrogen negatively regulates epidermal growth factor (EGF)-mediated signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 signaling in human EGF family receptor-overexpressing breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Nov;19(11):2660-70. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0439. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15976008
-
MNAR plays an important role in ERa activation of Src/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Steroids. 2008 Oct;73(9-10):901-5. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.028. Epub 2008 Jan 4. Steroids. 2008. PMID: 18261753 Review.
-
Methylation, a key step for nongenomic estrogen signaling in breast tumors.Steroids. 2010 Aug-Sep;75(8-9):560-4. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2010.01.013. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Steroids. 2010. PMID: 20116391 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis.J Clin Invest. 2013 Feb;123(2):630-45. doi: 10.1172/JCI64265. Epub 2013 Jan 16. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23321675 Free PMC article.
-
Functional regulation of pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox interacting protein 1 (PBXIP1/HPIP) in erythroid differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5600-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.289843. Epub 2011 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22187427 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of Pathogenomic Insights of Breast Cancer in Young Women.Cells. 2022 Jun 15;11(12):1927. doi: 10.3390/cells11121927. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741056 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2 restrains estrogen-mediated AKT activation by promoting TBK1-dependent HPIP degradation.Cell Death Differ. 2014 May;21(5):811-24. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.2. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24488098 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic PBX-interacting protein mediates cartilage degeneration during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 18;10(1):313. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08277-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30659184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edwards DP. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Manavathi B, Kumar R. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207:594–604. - PubMed
-
- Pedram A, Razandi M, Levin ER. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:1996–2009. - PubMed
-
- Cheskis BJ. J Cell Biochem. 2004;93:20–27. - PubMed
-
- Acconcia F, Barnes CJ, Kumar R. Endocrinology. 2006;147:1203–1212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

