Deficiency of Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b alters epigenetic modifications and suppresses an imprinting defect in the PWS/AS domain
- PMID: 17043311
- PMCID: PMC1619944
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1452206
Deficiency of Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b alters epigenetic modifications and suppresses an imprinting defect in the PWS/AS domain
Abstract
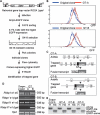
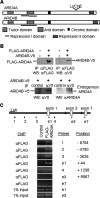
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS) are caused by deficiency of imprinted gene expression from paternal or maternal chromosome 15q11-q13, respectively. Genomic imprinting of the PWS/AS domain is regulated through a bipartite cis-acting imprinting center (PWS-IC/AS-IC) within and upstream of the SNRPN promoter. Here, we show that two Rb-binding protein-related genes, Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b, are involved in the regulation of imprinting of the IC. We recovered these two genes from gene trap mutagenesis selecting for altered expression of an Snrpn-EGFP fusion gene strategy. RBBP1/ARID4A is an Rb-binding protein. RBBP1/ARID4A interacts with RBBP1L1/ARID4B and with the Snrpn promoter, implying that both are part of a protein complex. To further elucidate their roles on regulation of imprinting, we deleted the Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b genes in mice. Combined homozygous deficiency for Rbbp1/Arid4a and heterozygous deficiency for Rbbp1l1/Arid4b altered epigenetic modifications at the PWS-IC with reduced trimethylation of histone H4K20 and H3K9 and reduced DNA methylation, changing the maternal allele toward a more paternal epigenotype. Importantly, mutations of Rbbp1/Arid4a, Rbbp1l1/Arid4b, or Rb suppressed an AS imprinting defect caused by a mutation at the AS-IC. These data identify Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b as new members of epigenetic complexes regulating genomic imprinting at the PWS/AS domain.
Figures


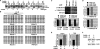

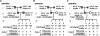
Similar articles
-
Identification of chromatin remodeling genes Arid4a and Arid4b as leukemia suppressor genes.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 Sep 3;100(17):1247-59. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn253. Epub 2008 Aug 26. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18728284 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Prader-Willi syndrome imprinting center on the DNA methylation landscape in the mouse brain.Epigenetics. 2014 Nov;9(11):1540-56. doi: 10.4161/15592294.2014.969667. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 25482058 Free PMC article.
-
An unexpected function of the Prader-Willi syndrome imprinting center in maternal imprinting in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034348. Epub 2012 Apr 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496793 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting defects on human chromosome 15.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;113(1-4):292-9. doi: 10.1159/000090844. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16575192 Review.
-
Structure and function of the human chromosome 15 imprinting center.J Cell Physiol. 1997 Nov;173(2):237-41. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199711)173:2<237::AID-JCP28>3.0.CO;2-B. J Cell Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9365529 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin mechanisms in genomic imprinting.Mamm Genome. 2009 Sep-Oct;20(9-10):544-56. doi: 10.1007/s00335-009-9223-4. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Mamm Genome. 2009. PMID: 19760321 Review.
-
Identification of imprinting regulators at the Meg3 differentially methylated region.Genomics. 2012 Sep;100(3):184-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2012.06.001. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22709555 Free PMC article.
-
Histone methylation in myelodysplastic syndromes.Epigenomics. 2011 Apr;3(2):193-205. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.9. Epigenomics. 2011. PMID: 22122281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of candidate imprinted genes in PWS subjects with atypical genetics: a possible inactivating mutation in the SNURF/SNRPN minimal promoter.J Hum Genet. 2007;52(4):297-307. doi: 10.1007/s10038-007-0109-6. Epub 2007 Jan 30. J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17262171
-
ARID3a from the ARID family: structure, role in autoimmune diseases and drug discovery.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Nov;44(11):2139-2150. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01134-2. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37488425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bannister, A.J., Kouzarides, T. Reversing histone methylation. Nature. 2005;436:1103–1106. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A.J., Zegerman, P., Partridge, J.F., Miska, E.A., Thomas, J.O., Allshire, R.C., Kouzarides, T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Bressler, J., Tsai, T.F., Wu, M.Y., Tsai, S.F., Ramirez, M.A., Armstrong, D., Beaudet, A.L. The SNRPN promoter is not required for genomic imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman domain in mice. Nat. Genet. 2001;28:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Buiting, K., Saitoh, S., Gross, S., Dittrich, B., Schwartz, S., Nicholls, R.D., Horsthemke, B. Inherited micro-deletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting centre on human chromosome 15. Nat. Genet. 1995;9:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Buiting, K., Lich, C., Cottrell, S., Barnicoat, A., Horsthemke, B. A 5-kb imprinting center deletion in a family with Angelman syndrome reduces the shortest region of deletion overlap to 880 bp. Hum. Genet. 1999;105:665–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
