Identifying systematic errors in quantitative dynamic-susceptibility contrast perfusion imaging by high-resolution multi-echo parallel EPI
- PMID: 17044140
- PMCID: PMC3985853
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.1107
Identifying systematic errors in quantitative dynamic-susceptibility contrast perfusion imaging by high-resolution multi-echo parallel EPI
Abstract
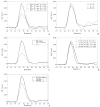
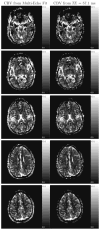
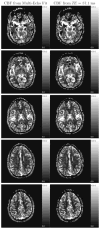
Several obstacles usually confound a straightforward perfusion analysis using dynamic-susceptibility contrast-based magnetic resonance imaging (DSC-MRI). In this work, it became possible to eliminate some of these sources of error by combining a multiple gradient-echo technique with parallel imaging (PI): first, the large dynamic range of tracer concentrations could be covered satisfactorily with multiple echo times (TE) which would otherwise result in overestimation of image magnitude in the presence of noise. Second, any bias from T(1) relaxation could be avoided by fitting to the signal magnitude of multiple TEs. Finally, with PI, a good tradeoff can be achieved between number of echoes, brain coverage, temporal resolution and spatial resolution. The latter reduces partial voluming, which could distort calculation of the arterial input function. Having ruled out these sources of error, a 4-fold overestimation of cerebral blood volume and flow remained, which was most likely due to the completely different relaxation mechanisms that are effective in arterial voxels compared with tissue. Hence, the uniform tissue-independent linear dependency of relaxation rate upon tracer concentration, which is usually assumed, must be questioned. Therefore, DSC-MRI requires knowledge of the exact dependency of transverse relaxation rate upon tracer concentration in order to calculate truly quantitative perfusion maps.
(c) 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
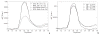
References
-
- Rempp KA, Brix G, Wenz F, Becker CR, Gückel F, Lorenz WJ. Quantification of regional cerebral blood flow and volume with dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 1994;193:637–641. - PubMed
-
- Østergaard L, Weisskoff RM, Chesler DA, Gyldensted C, Rosen BR. High resolution measurement of cerebral blood flow using intravascular tracer bolus passage. Part I: Mathematical approach and statistical analysis. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36:715–725. - PubMed
-
- van Osch MJP, Vonken EPA, Bakker CJG, Viergever MA. Correcting partial volume artifacts of the arterial input function in quantitative cerebral perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45:477–485. - PubMed
-
- van Osch MJP, Vonken EPA, Viergever MA, van der Grond J, Bakker CJG. Measuring the arterial input function with gradient echo sequences. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:1067–1076. - PubMed
-
- Kiselev VG. On the theoretical basis of perfusion measurements by dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:1113–1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

