Aromatase immunoreactivity in the bluehead wrasse brain, Thalassoma bifasciatum: immunolocalization and co-regionalization with arginine vasotocin and tyrosine hydroxylase
- PMID: 17045250
- PMCID: PMC1876742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.09.017
Aromatase immunoreactivity in the bluehead wrasse brain, Thalassoma bifasciatum: immunolocalization and co-regionalization with arginine vasotocin and tyrosine hydroxylase
Abstract
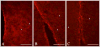
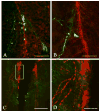
Sex steroid hormones regulate various neural functions that control vertebrate sociosexual behavior. A number of sex steroids can be synthesized de novo in the brain, including estrogens by the enzyme aromatase. Aromatase, the neuropeptides arginine vasotocin/vasopressin, and the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine have all been implicated in the control of male sexual and aggressive behavior in a variety of vertebrates. This study examined the expression of brain aromatase in the bluehead wrasse (Thalassoma bifasciatum), a teleost fish that exhibits socially controlled behavioral and gonadal sex change. We used immunocytochemistry (ICC) to characterize distributions of aromatase-immunoreactive (ir) cells, and to examine their relationship with AVT-ir neurons and tyrosine hydroxylase-ir (TH-ir) neurons in key sensory and integrative areas of the brain of this species. Aromatase-ir appeared to be in glial cell populations, and was found in the dorsal and ventral telencephalon, the preoptic area of the hypothalamus, and the lateral recess of the third ventricle, among other brain areas. Aromatase-ir fibers are closely associated with AVT-ir neurons throughout the preoptic area, indicating the potential for functional interactions. Aromatase-ir cell bodies and fibers were also co-regionalized with TH-ir neurons, suggesting possible interaction between the dopaminergic system and neural estrogen production. The presence of aromatase in brain regions important in the regulation of sexual and aggressive behavior suggests that local estrogen synthesis could regulate sex change through effects on signaling systems that subserve reproductive behavior and function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Variation in gene transcript profiles of two V1a-type arginine vasotocin receptors among sexual phases of bluehead wrasse (Thalassoma bifasciatum).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2012 Dec 1;179(3):451-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23063433
-
Hypothalamic arginine vasotocin mRNA abundance variation across sexes and with sex change in a coral reef fish.Brain Behav Evol. 2000 Feb;55(2):77-84. doi: 10.1159/000006643. Brain Behav Evol. 2000. PMID: 10838478
-
Social influences on the arginine vasotocin system are independent of gonads in a sex-changing fish.J Neurosci. 2003 May 15;23(10):4386-93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04386.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12764128 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of testosterone and its metabolites on aromatase-immunoreactive cells in the quail brain: relationship with the activation of male reproductive behavior.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):185-200. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00236-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603040 Review.
-
Steroid-induced plasticity in the sexually dimorphic vasotocinergic innervation of the avian brain: behavioral implications.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Nov;37(1-3):178-200. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00118-7. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11744086 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesencephalic origin of the inferior lobe in zebrafish.BMC Biol. 2019 Mar 8;17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0631-y. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 30849972 Free PMC article.
-
Fish and chips: functional genomics of social plasticity in an African cichlid fish.J Exp Biol. 2008 Sep;211(Pt 18):3041-56. doi: 10.1242/jeb.018242. J Exp Biol. 2008. PMID: 18775941 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of aromatase and two isozymes of 5α-reductase in the developing green anole forebrain.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Sep;24(9):1213-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02328.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22487458 Free PMC article.
-
Cyp19a1 (aromatase) expression in the Xenopus brain at different developmental stages.J Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Apr;26(4):226-36. doi: 10.1111/jne.12142. J Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24612124 Free PMC article.
-
In situ localization of vasotocin receptor gene transcripts in the brain-pituitary-gonadal axis of the catfish Heteropneustes fossilis: a morpho-functional study.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2019 Jun;45(3):885-905. doi: 10.1007/s10695-018-0590-1. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30506436
References
-
- Bakker J, Honda S, Harada N, Balthazart J. Restoration of male sexual behavior by adult exogenous estrogens in male aromatase knockout mice. Horm Behav. 2004;16:483–490. - PubMed
-
- Balthazart J, Baillien M, Ball GF. Rapid and reversible inhibition of brain aromatase activity. J Neuroendocrinol. 2001;13:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Balthazart J, Baillien M, Ball GF. Interactions between aromatase (estrogen synthase) and dopamine in the control of male sexual behavior in quail. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 2002;132:37–55. - PubMed
-
- Balthazart J, Ball GF. Is brain estradiol a hormone or neurotransmitter? Trends Neurosci. 2006;29(5):241–249. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari RK, Higa M, Komuro H, Nakamura S, Nakamura M. Gonadal restructuring and correlative steroid hormone profiles during natural sex change in protogynous honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra) Zool Sci. 2003;20:1399–1403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

