Nuclear HMGA1 nonhistone chromatin proteins directly influence mitochondrial transcription, maintenance, and function
- PMID: 17045586
- PMCID: PMC1823039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.09.014
Nuclear HMGA1 nonhistone chromatin proteins directly influence mitochondrial transcription, maintenance, and function
Abstract
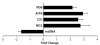
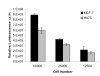
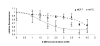
We have previously demonstrated that HMGA1 proteins translocate from the nucleus to mitochondria and bind to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) at the D-loop control region [G.A. Dement, N.R. Treff, N.S. Magnuson, V. Franceschi, R. Reeves, Dynamic mitochondrial localization of nuclear transcription factor HMGA1, Exp. Cell Res. 307 (2005) 388-401.] [11]. To elucidate possible physiological roles for such binding, we employed methods to analyze mtDNA transcription, mitochondrial maintenance, and other organelle functions in transgenic human MCF-7 cells (HA7C) induced to over-express an HA-tagged HMGA1 protein and control (parental) MCF-7 cells. Quantitative real-time (RT) PCR analyses demonstrated that mtDNA levels were reduced approximately 2-fold in HMGA1 over-expressing HA7C cells and flow cytometric analyses further revealed that mitochondrial mass was significantly reduced in these cells. Cellular ATP levels were also reduced in HA7C cells and survival studies showed an increased sensitivity to killing by 2-deoxy-D-glucose, a glycolysis-specific inhibitor. Flow cytometric analyses revealed additional mitochondrial abnormalities in HA7C cells that are consistent with a cancerous phenotype: namely, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increased mitochondrial membrane potential (Delta Psi(m)). Additional RT-PCR analyses demonstrated that gene transcripts from both the heavy (ND2, COXI, ATP6) and light (ND6) strands of mtDNA were up-regulated approximately 3-fold in HA7C cells. Together, these mitochondrial changes are consistent with many previous reports and reveal several possible mechanisms by which HMGA1 over-expression, a common feature of naturally occurring cancers, may affect tumor progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamic mitochondrial localization of nuclear transcription factor HMGA1.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Jul 15;307(2):388-401. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.04.004. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15893306
-
HMGA1 levels influence mitochondrial function and mitochondrial DNA repair efficiency.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;29(20):5426-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00105-09. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19687300 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 increases aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancers by stimulating HMGA1-mediated GLUT3 transcription.Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 15;72(16):4097-109. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0448. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22706202
-
The High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) Transcriptome in Cancer and Development.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(4):353-93. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160316152147. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26980699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mtDNA makes a U-turn for the mitochondrial nucleoid.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;23(9):457-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 27. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23721879 Review.
Cited by
-
Defects in the Mitochondrial Genome of Dogs with Recurrent Tumours.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13414. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413414. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769179 Free PMC article.
-
The Gene-Regulatory Footprint of Aging Highlights Conserved Central Regulators.Cell Rep. 2020 Sep 29;32(13):108203. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108203. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32997995 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sequence polymorphisms in the displacement loop region of mitochondrial DNA as a risk factor for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.J Clin Lab Anal. 2017 Sep;31(5):e22078. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22078. Epub 2016 Oct 5. J Clin Lab Anal. 2017. PMID: 27704598 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese Medicinal Formulation Guzhi Zengsheng Zhitongwan Modulates Chondrocyte Structure, Dynamics, and Metabolism by Controlling Multiple Functional Proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Nov 22;2018:9847286. doi: 10.1155/2018/9847286. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30596102 Free PMC article.
-
Mandatory role of HMGA1 in human airway epithelial normal differentiation and post-injury regeneration.Oncotarget. 2018 Feb 16;9(18):14324-14337. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24511. eCollection 2018 Mar 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29581847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reeves R. Molecular biology of HMGA proteins: hubs of nuclear function. Gene. 2001;277:63–81. - PubMed
-
- Banks GC, Li Y, Reeves R. Differential in vivo modifications of the HMGI(Y) nonhistone chromatin proteins modulate nucleosome and DNA interactions. Biochem. 2000;39:8333–8346. - PubMed
-
- Edberg DD, Bruce JE, Siems WF, Reeves R. In vivo post-translational modifications of the High Mobility Group A1a proteins in breast cancer cells of differing metastatic potential. Biochem. 2004;43:11500–11515. - PubMed
-
- Reeves R, Beckerbauer L. HMGI/Y proteins: flexible regulators of transcription and chromatin structure. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1519:13–29. - PubMed
-
- Lund T, Holtlund M, Fredrickson M, Laland SG. On the presence of two new high mobility group-like proteins in HeLa S3 Cells. FEBS (Fed. Eur. Biochem. Soc.) Lett. 1983;152:163–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

