Brain-specific phosphorylation of MeCP2 regulates activity-dependent Bdnf transcription, dendritic growth, and spine maturation
- PMID: 17046689
- PMCID: PMC3962021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.037
Brain-specific phosphorylation of MeCP2 regulates activity-dependent Bdnf transcription, dendritic growth, and spine maturation
Abstract
Mutations or duplications in MECP2 cause Rett and Rett-like syndromes, neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by mental retardation, motor dysfunction, and autistic behaviors. MeCP2 is expressed in many mammalian tissues and functions as a global repressor of transcription; however, the molecular mechanisms by which MeCP2 dysfunction leads to the neural-specific phenotypes of RTT remain poorly understood. Here, we show that neuronal activity and subsequent calcium influx trigger the de novo phosphorylation of MeCP2 at serine 421 (S421) by a CaMKII-dependent mechanism. MeCP2 S421 phosphorylation is induced selectively in the brain in response to physiological stimuli. Significantly, we find that S421 phosphorylation controls the ability of MeCP2 to regulate dendritic patterning, spine morphogenesis, and the activity-dependent induction of Bdnf transcription. These findings suggest that, by triggering MeCP2 phosphorylation, neuronal activity regulates a program of gene expression that mediates nervous system maturation and that disruption of this process in individuals with mutations in MeCP2 may underlie the neural-specific pathology of RTT.
Figures



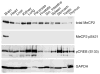
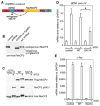
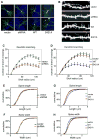
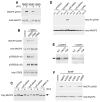
References
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Ariani F, Mari F, Pescucci C, Longo I, Bruttini M, Meloni I, Hayek G, Rocchi R, Zappella M, Renieri A. Realtime quantitative PCR as a routine method for screening large rearrangements in Rett syndrome: report of one case of MECP2 deletion and one case of MECP2 duplication. Hum Mutat. 2004;24:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Asaka Y, Jugloff DG, Zhang L, Eubanks JH, Fitzsimonds RM. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity is impaired in the Mecp2-null mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu T, Chelly J. Molecular genetics of Rett syndrome: when DNA methylation goes unrecognized. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:415–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

