Fine-tuning of awake prefrontal cortex neurons by clozapine: comparison with haloperidol and N-desmethylclozapine
- PMID: 17046721
- PMCID: PMC2910426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.05.016
Fine-tuning of awake prefrontal cortex neurons by clozapine: comparison with haloperidol and N-desmethylclozapine
Abstract
Background: Mechanisms underlying clozapine's better clinical efficacy in schizophrenia remain poorly understood. The prefrontal cortex (PFC) has been implicated as a primary site for the therapeutic effects of clozapine; however, evidence for how clozapine influences the activity of PFC neurons in behaviorally relevant contexts is lacking.
Methods: Ensemble single unit recording in awake rats was used to measure the activity of PFC neurons in response to clozapine, its main metabolite N-desmethylclozapine (DMClz), and the typical antipsychotic drug haloperidol during baseline conditions and after treatment with the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist MK801. Behavioral stereotypy was scored during recording.
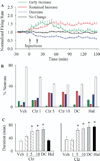
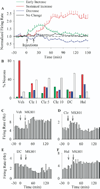
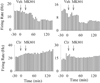
Results: Clozapine and DMClz but not haloperidol had an activity-dependent influence on spontaneous firing rate of PFC cells: they increased the activity of neurons with low baseline firing rates and decreased the activity of neurons with higher firing rates. Clozapine and DMClz but not haloperidol also reversed the effect of MK801 on PFC neuronal firing. This reversal was strongly correlated with blockade of MK801-induced behavioral stereotypy.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that clozapine has the capacity to fine-tune spontaneous and disrupted activity of PFC neurons. This effect might contribute, in part, to the therapeutic efficacy of clozapine in schizophrenia.
Figures


References
-
- Arango C, Breier A, McMahon R, Carpenter WJ, Buchanan R. The relationship of clozapine and haloperidol treatment response to prefrontal, hippocampal, and caudate brain volumes. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1421–1427. - PubMed
-
- Arvanov V, Liang X, Schwartz J, Grossman S, Wang R. Clozapine and haloperidol modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate- and non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated neurotransmission in rat prefrontal cortical neurons in vitro. J Pharm Exp Thera. 1997;283:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Arvanov V, Wang R. Clozapine, but not haloperidol, prevents the functional hyperactivity of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat cortical neurons induced by subchronic administration of phencyclidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289:1000–1006. - PubMed
-
- Baeg EH, Kim YB, Jang J, Kim HT, Mook-Jung I, Jung MW. Fast spiking and regular spiking neural correlates of fear conditioning in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Cereb Cortex. 2001;11:441–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

