A phase II trial of gefitinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations
- PMID: 17047648
- PMCID: PMC2360715
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603393
A phase II trial of gefitinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations
Abstract
Retrospective analysis has shown that activating mutations in exons 18-21 of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene are a predictor of response to gefitinib. We conducted a phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gefitinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR mutations. Patients with stage IIIB or IV chemotherapy-naïve NSCLC with EGFR mutation were treated with 250 mg gefitinib daily. For mutational analysis, DNA was extracted from paraffin-embedded tissues and EGFR mutations were analysed by direct sequence of PCR products. Twenty (24%) of the 82 patients analysed had EGFR mutations (deletions in or near E746-A750, n=16; L858R, n=4). Sixteen patients were enrolled and treated with gefitinib. Twelve patients had objective response and response rate was 75% (95% CI, 48-93%). After a median follow-up of 12.7 months (range, 3.1-16.8 months), 10 patients demonstrated disease progression, with median progression-free survival of 8.9 months (95% CI, 6.7-11.1 months). The median overall survival time has not yet been reached. Most of the toxicities were mild. This study showed that gefitinib is very active and well tolerated as first-line therapy for advanced NSCLC with EGFR mutations.
Figures
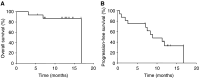
Comment in
-
Are exon 19 deletions and L858R EGFR mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer clinically different?Br J Cancer. 2007 Jan 29;96(2):399; author reply 400. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603564. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17224926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ando M, Okamoto I, Yamamoto N, Takeda K, Tamura K, Seto T, Ariyoshi Y, Fukuoka M (2006) Predictive factors for interstitial lung disease, antitumor response, and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol 24: 2549–2556 - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL (2002) Overview of epidermal growth factor receptor biology and its role as a therapeutic target in human neoplasia. Semin Oncol 29: 3–9 - PubMed
-
- Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Haserlat SM, Harris PL, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Sgroi DC, Muir B, Riemenschneider MJ, Iacona RB, Krebs AD, Johnson DH, Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Fukuoka M, Kris MG, Baselga J, Ochs JS, Haber DA (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non-small-cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. J Clin Oncol 23: 8081–8092 - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Gregorc V, Rossi E, Cancellieri A, Magrini E, Paties CT, Ceresoli G, Lombardo L, Bartolini S, Calandri C, de Rosa M, Villa E, Crino L (2003) Gefitinib in pretreated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): analysis of efficacy and correlation with HER2 and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. J Clin Oncol 21: 2658–2663 - PubMed
-
- Chan SK, Gulick WJ, Hill ME (2006) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer – Search and destroy. Eur J Cancer 42: 17–23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

