An extended window of opportunity for G-CSF treatment in cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 17049076
- PMCID: PMC1633735
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-4-36
An extended window of opportunity for G-CSF treatment in cerebral ischemia
Abstract
Background: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is known as a powerful regulator of white blood cell proliferation and differentiation in mammals. We, and others, have shown that G-CSF is effective in treating cerebral ischemia in rodents, both relating to infarct size as well as functional recovery. G-CSF and its receptor are expressed by neurons, and G-CSF regulates apoptosis and neurogenesis, providing a rational basis for its beneficial short- and long-term actions in ischemia. In addition, G-CSF may contribute to re-endothelialisation and arteriogenesis in the vasculature of the ischemic penumbra. In addition to these trophic effects, G-CSF is a potent neuroprotective factor reliably reducing infarct size in different stroke models.
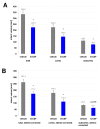
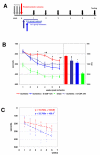
Results: Here, we have further delayed treatment and studied effects of G-CSF on infarct volume in the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model and functional outcome in the cortical photothrombotic model. In the MCAO model, we applied a single dose of 60 microg/kg bodyweight G-CSF in rats 4 h after onset of ischemia. Infarct volume was determined 24 h after onset of ischemia. In the rat photothrombotic model, we applied 10 microg/kg bodyweight G-CSF daily for a period of 10 days starting either 24 or 72 h after induction of ischemia. G-CSF both decreased acute infarct volume in the MCAO model, and improved recovery in the photothrombotic model at delayed timepoints.
Conclusion: These data further strengthen G-CSF's profile as a unique candidate stroke drug, and provide an experimental basis for application of G-CSF in the post-stroke recovery phase.
Figures
References
-
- Begley CG, Lopez AF, Nicola NA, Warren DJ, Vadas MA, Sanderson CJ, Metcalf D. Purified colony-stimulating factors enhance the survival of human neutrophils and eosinophils in vitro: a rapid and sensitive microassay for colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1986;68:162–166. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

