Interleukin-6 facilitates lipopolysaccharide-induced disruption in working memory and expression of other proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal neuronal cell layers
- PMID: 17050710
- PMCID: PMC6674759
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3376-06.2006
Interleukin-6 facilitates lipopolysaccharide-induced disruption in working memory and expression of other proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal neuronal cell layers
Abstract
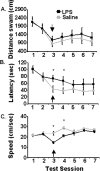
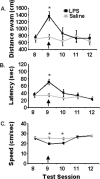
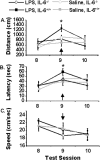
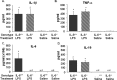
Proinflammatory cytokines inhibit learning and memory but the significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in acute cognitive deficits induced by the peripheral innate immune system is not known. To examine the functional role of IL-6 in hippocampus-mediated cognitive impairments associated with peripheral infections, C57BL6/J (IL-6(+/+)) and IL-6 knock-out (IL-6(-/-)) mice were trained in a matching-to-place version of the water maze. After an acquisition phase, IL-6(+/+) mice injected intraperitoneally with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exhibited deficits in working memory. However, IL-6(-/-) mice were refractory to the LPS-induced impairment in working memory. To determine the mechanism by which IL-6 deficiency conferred protection from disruption in working memory, plasma IL-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), c-Fos immunoreactivity in the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), and steady-state levels of IL-1beta and TNFalpha mRNA in neuronal layers of the hippocampus were determined in IL-6(+/+) and IL-6(-/-) mice after injection of LPS. Plasma IL-1beta and TNFalpha and c-Fos immunoreactivity in the NTS were increased similarly in IL-6(+/+) and IL-6(-/-) mice after LPS, indicating high circulating levels of IL-1beta and TNFalpha and activation of vagal afferent pathways were not sufficient to disrupt working memory in the absence of IL-6. However, the LPS-induced upregulation of IL-1beta and TNFalpha mRNA that was evident in hippocampal tissue of IL-6(+/+) mice was greatly attenuated or entirely absent in IL-6(-/-) mice. Collectively, these data suggest that humoral and neural immune-to-brain communication pathways are intact in IL-6-deficient mice but that, in the absence of IL-6, the central cytokine compartment is hyporesponsive.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cognitive deficits in interleukin-10-deficient mice after peripheral injection of lipopolysaccharide.Brain Behav Immun. 2009 Aug;23(6):794-802. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.02.020. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2009. PMID: 19272439 Free PMC article.
-
Central and peripheral immune responses to low-dose lipopolysaccharide in a mouse model of the 15q13.3 microdeletion.Cytokine. 2020 Feb;126:154879. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154879. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31629107
-
Neuroinflammation and disruption in working memory in aged mice after acute stimulation of the peripheral innate immune system.Brain Behav Immun. 2008 Mar;22(3):301-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.08.014. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2008. PMID: 17951027 Free PMC article.
-
Why Do Levels Of Anti-inflammatory Cytokines Increase During Memory Acquisition?Neuroscience. 2021 Oct 1;473:159-169. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 34418518 Review.
-
Modulation of learning and memory by cytokines: signaling mechanisms and long term consequences.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Nov;115:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 25151944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of galectin-9 and artemin as biomarkers in long COVID with chronic fatigue syndrome: links to inflammation and cognitive function.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1443363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1443363. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39386210 Free PMC article.
-
Spermine reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced memory deficit in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Jan 9;12:3. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0220-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25573647 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin inhibits microglia and alters hippocampal-dependent spatial working memory in aged mice.J Nutr. 2010 Oct;140(10):1892-8. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.123273. Epub 2010 Aug 4. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20685893 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-synuclein pre-formed fibrils injected into prefrontal cortex primarily spread to cortical and subcortical structures and lead to isolated behavioral symptoms.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 15:2023.01.31.526365. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.31.526365. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(1):81-94. doi: 10.3233/JPD-230129. PMID: 36778400 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CX3CR1 protein signaling modulates microglial activation and protects against plaque-independent cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 16;286(37):32713-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.254268. Epub 2011 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21771791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai K, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y, Nishiyama N. Deterioration of spatial learning performances in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001;87:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Aubert A, Vega C, Dantzer R, Goodall G. Pyrogens specifically disrupt the acquisition of a task involving cognitive processing in the rat. Brain Behav Immun. 1995;9:129–148. - PubMed
-
- Balschun D, Wetzel W, del Rey A, Pitossi F, Schneider H, Zuschratter W, Besedovsky HO. Interleukin-6: a cytokine to forget. FASEB J. 2004;18:1788–1790. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Memory for context is impaired by a post context exposure injection of interleukin-1 beta into dorsal hippocampus. Behav Brain Res. 2002;134:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Biedenkapp JC, Sprunger DB, Wright-Hardesty KJ, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Peripheral infection and aging interact to impair hippocampal memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:723–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
