Natural killer cell and hepatic cell interaction via NKG2A leads to dendritic cell-mediated induction of CD4 CD25 T cells with PD-1-dependent regulatory activities
- PMID: 17052247
- PMCID: PMC2265878
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02479.x
Natural killer cell and hepatic cell interaction via NKG2A leads to dendritic cell-mediated induction of CD4 CD25 T cells with PD-1-dependent regulatory activities
Abstract
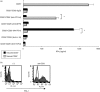
Natural killer (NK) cells have the ability to control dendritic cell (DC)-mediated T cell responses. However, the precise mechanisms by which NK receptor-mediated regulation of NK cells determines the magnitude and direction of DC-mediated T cell responses remain unclear. In the present study, we applied an in vitro co-culture system to examine the impact of NK cells cultured with hepatic cells on DC induction of regulatory T cells. We found that interaction of NK cells and non-transformed hepatocytes (which express HLA-E) via the NKG2A inhibitory receptor resulted in priming of DCs to induce CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells with regulatory properties. NKG2A triggering led to characteristic changes of the cytokine milieu of co-cultured cells; an increase in the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta involved in the generation of this specific type of DC, and a decrease in the tumour necrosis factor-alpha capable of antagonizing the effect of TGF-beta. The regulatory cells induced by NK cell-primed DCs exert their suppressive actions through a negative costimulator programmed death-1 (PD-1) mediated pathway, which differs from freshly isolated CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells. These findings provide new insight into the role of NK receptor signals in the DC-mediated induction of regulatory T cells.
Figures

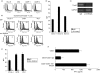

Similar articles
-
The natural killer cell-mediated killing of autologous dendritic cells is confined to a cell subset expressing CD94/NKG2A, but lacking inhibitory killer Ig-like receptors.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jun;33(6):1657-66. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323986. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12778484
-
Dendritic cells partially abrogate the regulatory activity of CD4+CD25+ T cells present in the human peripheral blood.Int Immunol. 2007 Mar;19(3):227-37. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxl139. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Int Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17289657
-
Negative regulation of NK cell activities by inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A leads to altered NK cell-induced modulation of dendritic cell functions in chronic hepatitis C virus infection.J Immunol. 2004 Nov 15;173(10):6072-81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.10.6072. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15528343
-
[CD94/NKG2A--a kind of inhibitory receptor belonging to C-type lectin superfamily].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2002 Dec;24(6):653-5. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2002. PMID: 12905700 Review. Chinese.
-
Cytokine-driven regulation of NK cell functions in tumor immunity: role of the MICA-NKG2D system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007 Feb-Apr;18(1-2):159-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.01.013. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007. PMID: 17324607 Review.
Cited by
-
VEGF Inhibitors Improve Survival Outcomes in Patients with Liver Metastases across Cancer Types-A Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 16;15(20):5012. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205012. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Nov;10(11):753-66. doi: 10.1038/nri2858. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20972472 Review.
-
Organ-specific features of natural killer cells.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Sep 23;11(10):658-71. doi: 10.1038/nri3065. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21941294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into Human Intrahepatic NK Cell Function From Single Cell RNA Sequencing Datasets.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 22;12:649311. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.649311. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33828559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complex myeloid network of the liver with diverse functional capacity at steady state and in inflammation.Front Immunol. 2015 Apr 20;6:179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00179. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25941527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shevach EM. CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:389–400. - PubMed
-
- Belkald Y, Piccirillo CA, Mendez S, Shevach EM, Sacks DL. CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature. 2002;420:502–7. - PubMed
-
- Wang HY, Lee DA, Peng G, Guo Z, Li Y, Kiniwa Y, Shevach EM, Wang RF. Tumour-specific human CD4+ regulatory T cells and their ligands: implication for immunotherapy. Immunity. 2004;20:107–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

