Anticholinergic drugs versus placebo for overactive bladder syndrome in adults
- PMID: 17054185
- PMCID: PMC8729219
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003781.pub2
Anticholinergic drugs versus placebo for overactive bladder syndrome in adults
Update in
-
Oral anticholinergic drugs versus placebo or no treatment for managing overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 9;5(5):CD003781. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003781.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37160401 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: Around 16% of adults have symptoms of overactive bladder (urgency with frequency and/or urge incontinence). The prevalence increases with age. Anticholinergic drugs are commonly used to treat this condition.
Objectives: To determine the effects of anticholinergic drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Trials Register (searched 14 June 2005) and the reference lists of relevant articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised trials in adults with overactive bladder syndrome that compared an anticholinergic drug with placebo treatment or no treatment.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewer authors independently assessed eligibility, trial quality and extracted data. Data were processed as described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2005).
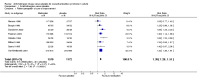
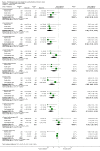
Main results: Sixty -one trials, 42 with parallel-group designs and 19 crossover trials were included (11,956 adults). Most trials were described as double-blind but were variable in other aspects of quality. The crossover trials did not present data in a way that allowed inclusion in the meta-analysis. Nine medications were tested: darifenacin; emepronium bromide or carrageenate; oxybutynin; propiverine; propantheline; tolterodine; trospium chloride; and solifenacin. One trial included the newer, slow release formulation of tolterodine. At the end of the treatment period, cure or improvement (relative risk (RR) 1.39, 95% CI 1.28 to 1.51), difference in leakage episodes in 24 hours (weighted mean difference (WMD) -0.54; 95% CI -0.67 to -0.41) and difference in number of voids in 24 hours (WMD -0.69; 95% CI -0.84 to -0.54) were statistically significant favouring medication. Statistically significant but modest sized improvements in quality of life scores were reported in recently completed trials. There was three times the rate of dry mouth in the medication group (RR 3.00 95% CI 2.70 to 3.34) but no statistically significant difference in withdrawal (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.36). Sensitivity analysis, while limited by small numbers of trials, showed little likelihood that the effects were modified by age, sex, diagnosis, or choice of drug.
Authors' conclusions: The use of anticholinergic drugs by people with overactive bladder syndrome results in statistically significant improvements in symptoms. Recent trials suggest that this is associated with modest improvement in quality of life. Dry mouth is a common side effect of therapy but did not seem to have an effect on the numbers of withdrawals. It is not clear whether any benefits are sustained during long-term treatment or after treatment stops.
Conflict of interest statement
Gaye Ellis was the study co‐ordinator for one of the centres in a multi centre/multinational trial included in the review. None declared for Peter Herbison and Jean Hay‐Smith, Nabi Ghulam and June Cody.
Figures






Update of
-
Anticholinergic drugs versus placebo for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD003781. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003781. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD003781. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003781.pub2. PMID: 12137711 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abrams 1996 {published data only}
-
- Abrams P, Jackson S, Mattiasson A, Krishnan K, Haendler L. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo controlled, dose ranging study of the safety and efficacy of tolterodine in patients with hyperreflexia. Proceedings of the International Continence Society 26th Annual Meeting. 1996:276‐7.
Abrams 1998 {published data only}
-
- Abrams P, Freeman R, Anderstrom C, Mattiasson A. Tolterodine, a new antimuscarinic agent: as effective but better tolerated than oxybutynin in patients with an overactive bladder. British Journal of Urology 1998;81:801‐10. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Freeman RN, Anderstrom C, Mattiasson A. Efficacy and tolerability of tolterodine vs. oxybutynin and placebo in patients with detrusor instability. Journal of Urology Annual Meeting. 1997; Vol. 157(4):103.
Abrams 2001 {published data only}
-
- Abrams P, Kaplan S, Millard R. Tolterodine treatment is safe in men with bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) and symptomatic detrusor overactivity (DO). Proceedings of the International Continence Society, 32nd Annual Meeting,Seoul. 2001.
Alloussi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Alloussi S, Laval K U, Ballering‐Bruhl B, Grobe‐Freese M, Bulitta M, Schafer M. Trospium chloride (Spasmo‐lyt) in patients with motor urge syndrome (detrusor instability): a double‐blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Clinical Research 1998;1:439‐51.
Bagger 1985 {published data only}
-
- Bagger P, Fischer‐Rasmussen W, Hansen RI. Emepronium carregeenate: clinical effects and urinary excretion in treatment of female urge incontinence. Scandanavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1985;19:31‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bagger PV, Fischer‐Rasmussen W. [Emepronium carragenate in the treatment of female urinary motor‐urge incontinence]. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society; 1984 Sep 13‐15; Innsbruck. 1984:304.
Bono 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bono AV, Marconi AM, Gianneo E. Oxybutynin for Unstable Bladder. A preliminary placebo controlled trial [L'ossibutinina cloridrato nella vescica instabile pura (Italian)]. Urologia 1982;49:764‐8.
Burgio 1998 {published data only}
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS. Combined behavioral and drug therapy for urge incontinence in older women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48:370‐4. - PubMed
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS, Hardin M, McDowell BJ, Dombrowski M, et al. Behavioral vs drug treatment for urge urinary incontinence in older women. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280(23):1995‐2000. - PubMed
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Roth DL, Goode PS. Psychological improvements associated with behavioral and drug treatment of urge incontinence in older women. Journal of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences 2001;56B(1):46‐51. - PubMed
Cardozo 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cardozo L, Chapple CR, Toozs‐Hobson P, Grosse‐Freese M, Bulitta M, Lehmacher W, et al. Efficacy of trospium chloride in patients with detrusor instability: a placebo‐controlled, randomised, double‐blind, multicentre clinical trial. British Journal of Urology International 2000;85:659‐64. - PubMed
Cardozo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cardozo L, Lisec M, Millard R, Vierssen Trip O, Kuzmin I, Drogendijk TE, et al. Randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of the once daily antimuscarinic agent solifenacin succinate in patients with overactive bladder. Journal of Urology 2004;172(5(Pt 1 of 2)):1919‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kelleher CJ, Cardozo L, Chapple CR, Haab F, Ridder AM. Improved quality of life in patients with overactive bladder symptoms treated with solifenacin. BJU International 2005;95(1):81‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chaliha 1998 {published data only}
-
- Chaliha C, Halaska M, Stanton S. Trospium chloride for the treatment of detrusor instability: a placebo‐controlled dose‐finding study. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;105(Suppl 17):276.
Chapple 2004a {published data only}
-
- Chapple CR, Arano P, Bosch JHR, Ridder D, Kramer G, Ridder AM. YM905 appears effective and well tolerated in patients with symptomatic idiopathic detrusor overactivity in a European placebo‐ and tolterodine‐controlled, phase‐II, dose‐finding study (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(4):381‐2. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Chapple CR, Arano P, Bosch JL, Ridder D, Kramer AE, Ridder AM. Solifenacin appears effective and well tolerated in patients with symptomatic idiopathic detrusor overactivity in a placebo‐ and tolterodine‐controlled phase 2 dose‐finding study. BJU International 2004;93(1):71‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kelleher CJ, Cardozo L, Chapple CR, Haab F, Ridder AM. Improved quality of life in patients with overactive bladder symptoms treated with solifenacin. BJU International 2005;95(1):81‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chapple 2004b {published data only}
-
- Chapple CR, Rechberger T, Al Shukri S, Meffan P, Everaert K, Huang M, et al. Randomized, double‐blind placebo‐ and tolterodine‐controlled trial of the once‐daily antimuscarinic agent solifenacin in patients with symptomatic overactive bladder. BJU International 2004;93(3):303‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coombes 1996 {published data only}
-
- Coombes GM, Millard RJ. A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial of penthienate in the treatment of detrusor instability (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society 24th Annual Meeting; 1994 Aug 30 ‐ Sept 2; Prague, Czech Republic; 1994 104. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Coombes GM, Millard RJ. Urinary urge incontinence: randomised crossover trials of penthienate versus placebo and propantheline. Medical Journal of Australia 1996;165(9):473‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davila 2001 {published data only}
-
- Davila GW, Sanders S, for the Transdermal Oxybutynin Study Group. Transdermal oxybutynin: A multi‐center, prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study in adults with urge urinary incontinence. International Urogynecology Journal 2001;12(Suppl 3):S43.
-
- Davila GW, Sanders SW, Lyttle S, Gittelman MC, Zinner N, Saltzstein DR et al for the Transdermal Oxybutynin Study Group. Transdermal oxybutynin is safe, effective, and improves quality of life in patients with overactive bladder. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001;20(4):426‐7.
Di Stasi 2001a {published data only}
-
- Stasi SM, Giannantoni A, Vespasiani G, Navarra P, Capelli G, Massoud R, et al. Intravesical electromotive administration of oxybutynin in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia unresponsive to standard anticholinergic regimens. Journal of Urology 2001;165:491‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dmochowski 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dmochowski RR, Sand PK, Zinner NR, Gittelman MC, Davila GW, Sanders SW, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of transdermal oxybutynin and oral tolterodine versus placebo in previously treated patients with urge and mixed urinary incontinence. Urology 2003;62(2):237‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dorschner 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dorschner W, Stolzenburg JU, Griebenow R, Halaska M, Schubert G, Murtz G, et al. Efficacy and cardiac safety of propiverine in elderly patients ‐ a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical study. European Urology 2000;37:702‐8. - PubMed
Drutz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Drutz H, Appell RA. Clinical efficacy and safety of Tolterodine vs Oxybutynin and placebo in patients with unstable bladder. Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1997;Suppl 167(5):24.
-
- Drutz HP, Appell RA. Enhanced tolerability of Tolterodine compared to Oxybutynin in a controlled clinical study. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1997;8(1):S14. - PubMed
-
- Drutz HP, Appell RA, Gleason D, Klimberg I, Radomski S. Clinical efficacy and safety of tolterodine compared to oxybutynin and placebo in patients with overactive bladder. International Urogynecology Journal 1999;10:283‐9. - PubMed
Freeman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Freeman R, Hill S, Millard R, Slack M, Sutherst J, Tolterodine Study Group. Reduced perception of urgency in treatment of overactive bladder with extended‐release tolterodine. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;102(3):605‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goode 2002 {published data only}
-
- Goode PS, Burgio KL, Locher JL, Umlauf MG, Lloyd LK, Roth DL. Urodynamic changes associated with behavioral and drug treatment of urge incontinence in older women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50(5):808‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Haab 2004 {published data only}
-
- Haab F, Stewart L, Dwyer P. Darifenacin, an M3 selective receptor antagonist, is an effective and well‐tolerated once‐daily treatment for overactive bladder. European Urology 2004;45(4):420‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Halaska 1994 {published data only}
-
- Halaska M, Dorschner W, Frank M. Treatment of urgency and incontinence in elderly patients with propiverine hydrochloride. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1994;13(4):428‐30.
Homma 2003 {published data only}
-
- Homma Y, Kawabe K. Health‐related quality of life of Japanese patients with overactive bladder treated with extended‐release tolterodine or immediate‐release oxybutynin: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. World Journal of Urology 2004;22(4):251‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Homma Y, Paick JS, Lee JG, Kawabe K, Japanese and Korean Tolterodine Study Group. Clinical efficacy and tolerability of extended‐release tolterodine and immediate‐release oxybutynin in Japanese and Korean patients with an overactive bladder: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. BJU International 2003;92(7):741‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jacquetin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jacquetin B, Wyndaele JJ. Tolterodine reduces the number of incontinence episodes in patients with an overactive bladder. European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2001;98:97‐102. - PubMed
-
- Jacquetin B, Wyndaele JJ. Tolterodine reduces the number of incontinence episodes in patients with detrusor overactivity. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1997;8(1):S30.
Jonas 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jonas U, Hofner K, Madersbacher H. Efficacy and safety of two doses of tolterodine versus placebo in patients with detrusor overactivity and symptoms of frequency, urge incontinence, and urgency: urodynamic evaluation. World Journal of Urology 1997;15:144‐51. - PubMed
-
- Jonas U, Hofner K, Madersbacher H, Holmdahl TH. Efficacy and safety of two doses of Tolterodine compared to placebo in patients with detrusor overactivity. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1997;16(5):477‐8. - PubMed
Junemann 1999 {published data only}
-
- Junemann KP, Fusgen I. Placebo‐controlled, randomised, double‐blind, multicentre clinical trial on the efficacy and tolerability of 1 x 40 mg and 2 x 40 mg trospium chloride (Spasmo‐lyt) daily for 3 weeks in patients with urge‐syndrome. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1999;18(4):375‐6.
Junemann 2000 {published data only}
-
- Junemann KP, Al‐Shukri S. Efficacy and tolerability of trospium chloride and tolterodine in 234 patients with urge‐syndrome: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicentre clinical trial. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2000;19(4):488‐90.
Khullar 2004 {published data only}
-
- Khullar V, Hill S, Laval KU, Schiotz HA, Jonas U, Versi E. Treatment of urge‐predominant mixed urinary incontinence with tolterodine extended release: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Urology 2004;64(2):269‐74; discussion 274‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kramer 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kramer AEJL, Zeegers AGM, Kiesswetter H, Jonas U. Drug treatment of urgency: a double blind trial of cetiprin®, dridase®, urispas® and placebo [Medicamenteuze behandeling van overmatige mictiedrang: Dubbel‐blind onderzoek van cetiprin®, dridase®, urispas® en placebo (Flemish)]. TGO tijdschrift voor Therapie, Geneesmiddel, en Onderzoek 1987;12(7):256‐61.
Landis 2004 {published data only}
-
- Landis JR, Kaplan S, Swift S, Versi E. Efficacy of antimuscarinic therapy for overactive bladder with varying degrees of incontinence severity. Journal of Urology 2004;171(2 (Pt 1)):752‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Madersbacher 1999 {published data only}
-
- Halaska M, Madersbacher H, Voigt R, Hofner K, Martan A. Propiverine in patients with urgency and urge incontinence ‐ a placebo controlled, multicenter study comparing its tolerability and efficacy with oxybutynin. International Urogynaecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2000;11(Suppl 1):46.
-
- Madersbacher H, Halaska M, Voigt R, Alloussi S, Hofner K. A placebo‐controlled, multicentre study comparing the tolerability and efficacy of propiverine and oxybutynin in patients with urgency and urge incontinence. British Journal of Urology International 1999;84:646‐51. - PubMed
-
- Madersbacher H, Halaska M, Voigt R, Alloussi S, Hofner K. A urodynamically controlled multicenter study in patients with urge incontinence: tolerability and efficacy of propiverine hydrochloride in comparison to oxybutynin. Proceedings of the International Continence Society 27th Annual Meeting. 1997:153‐4.
Malone‐Lee 2001 {published data only}
-
- Malone‐Lee JG, Walsh B, Maugourd MF and the Tolterodine in the Elderly Study Group. The safety and clinical efficacy of two doses of Tolerodine, compared to placebo in elderly patients. Proceedings of the International Continence Society. 1997:155‐6.
-
- Malone‐Lee JG, Walsh JB, Maugourd M‐F, and the Tolterodine in the Elderly Study Group. Tolterodine: A safe and effective treatment for older patients with overactive bladder. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 2001;49:700‐5. - PubMed
Massey 1986 {published data only}
-
- Massey JA, Abrams P. Dose titration in clinical trials. An example using emepronium carrageenate in detrusor instability. British Journal of Urology 1986;58:125‐8. - PubMed
-
- Massey JA, Abrams PH. Dose‐titrated emepronium carrageenate for detrusor instability. Proceedings of the International Continence Society 14th Annual Meeting. 1984:109‐10.
Meyhoff 1983 {published data only}
-
- Meyhoff H H, Gerstenberg TC, Nordling J. Placebo ‐ the drug of choice in female motor urge incontinence?. British Journal of Urology 1983;55:34‐7. - PubMed
Millard 1999 {published data only}
-
- Millard R, Tuttle J, Moore K, Susset J, Clarke B, Dwyer P, Davis B. Clinical efficacy and safety of tolterodine compared to placebo in detrusor overactivity. Journal of Urology 1999;161:1551‐5. - PubMed
-
- Moore K, Millard R, Dwyer P, Tuttle J. A randomized controlled multicentre trial of Tolterodine in detrusor instability/hyperreflexia. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1997;8(1):S129.
-
- Rosamilia A, Dwyer PL, Clarke B, Moore K, Millard RP, Tuttle J. The clinical efficacy and safety of two doses of Tolterodine in detrusor instability. Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1997;167(5):24.
Moisey 1980 {published data only}
-
- Bary PR, Moisey CU, Stephenson TP, Brendler CB. The urodynamic and subjective results of treatment of detrusor instability with oxybutynin chloride. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1981;78:313‐9. - PubMed
-
- Moisey CU, Stephenson TP, Brendler CB. The urodynamic and subjective results of treatment of detrusor instability with oxybutynin chloride. British Journal of Urology 1980;52:472‐5. - PubMed
Moore 1990 {published data only}
-
- Moore KH, Hay DM, Imrie AE, Watson A, Goldstein M. Oxybutynin hydrochloride (3mg) in the treatment of women with idiopathic detrusor instabilty. British Journal of Urology 1990;66:479‐85. - PubMed
-
- Moore KH, Hay DM, Imrie AH, Cockin J. Randomized double blind placebo‐controlled trial of oxybutynin in females with detrusor instability. Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society. 1987:137‐8.
-
- Moore KH, Sutherst JR. Response to treatment of detrusor instability in relation to psychoneurotic status. British Journal of Urology 1990;66:486‐90. - PubMed
Murray 1984 {published data only}
-
- Murray KHA, Patterson JR, Stephenson TP. A double‐blind three way cross over placebo controlled trial of cystrin and cetiprin novum. Proceedings of the 14th annual Meeting of the International Continence Society. 1984:454.
Rentzhog 1998 {published data only}
-
- Rentzhog SL, Stanton L, Cardozo L, Nelson E, Fall M, Abrams P. Efficacy and safety of tolterodine in patients with detrusor instability: a dose‐ranging study. British Journal of Urology 1998;81:42‐8. - PubMed
Riva 1984 {published data only}
-
- Riva D, Casolati E. Oxybutynin chloride in the treatment of female idiopathic bladder instability. Results from double blind treatment. Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;XI(1‐2):37‐42. - PubMed
Rosario 1995a {published data only}
-
- Rosario DJ, Leaker BR, Noble JG, Milroy E, Chapple CR. A double‐blind placebo controlled crossover study of the effects of single doses of darifenacin on cystometric parameters in patients with detrusor instability. Proceedings of the 25th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society. 1995:223.
Rosario 1995b {published data only}
-
- Rosario DJ, Leaker BR, Smith DJ, Chapple CR. A pilot study of the effects of multiple doses of the M3 muscarinic receptor agonist darifenacin on ambulatory parameters of detrusor activity in patients with detrusor instability (Abstract 36). Neurourology and Urodynamics 1995;14(5):464‐5.
SerranoBrambila 2000 {published data only}
-
- Serrano Brambila EA, Avila RGQ, Monterrubio JLL, Aranda JM. Evaluation of the effectiveness and tolerance of oxybutynin in the treatment of unstable bladder [Evaluación de la efectividad y tolerancia de la oxibutinina en la tratamiento de la vejiga inestable en la mujer (Spanish)]. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de México 2000;68:174‐81. - PubMed
Stohrer 1991 {published data only}
-
- Stohrer M, Bauer P, Giannetti BM, Richter R, Burgdorfer H, Murtz G. Effect of trospium chloride on urodynamic parameters in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia due to spinal cord injuries. Urologia Internationalis 1991;47:138‐43. - PubMed
Stohrer 1999 {published data only}
-
- Stohrer M, Madersbacher H, Richter R, Wehnert J, Dreikorn K. Efficacy and safety of propiverine in SCI‐patients suffering from detrusor hyperreflexia ‐ A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clnical trial. Spinal Cord 1999;37:196‐200. - PubMed
Szonyi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Collas DM, Szonyi G, Ding YY, Malone‐Lee JG. Oxybutynin with bladder retraining for detrusor instability in the elderly ‐ a placebo controlled trial. Age and Ageing 1994;23(Suppl. 2):9. - PubMed
-
- Szonyi G, Collas DM, Ding YY, Malone‐Lee JG. Oxybutynin with bladder retraining for detrusor instability in elderly people: A randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 1995;24:287‐91. - PubMed
Tago 1990 {published data only}
-
- Tago K, Ueno A, Takayasu H. Clinical study of propiverine hydrochloride for the treatment of patients with urinary frequency and incontinence. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1990;9(4):337‐8.
Takayasu 1990 {published data only}
-
- Takayasu H, Ueno A, Tsutida S, Koiso K, Kurita K, Kawabe K, et al. Clinical effects of propiverine hydrochloride in the treatment of urinary frequency and incontinence associated with detrusor overactivity: a double blind, parallel, placebo controlled multicenter study. Igaku No Ayumi (Progress in Medicine) 1990;153:459‐71. [MEDLINE: ]
Tapp 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cardozo LD, Cooper D, Versi E. Oxybutynin chloride in the management of idiopathic detrusor instability (Abstract 88). Neurourology and Urodynamics 1987;6(3):256‐7.
-
- Tapp AJS, Cardozo LD, Versi E, Cooper D. The treatment of detrusor instability in post‐menopausal women with oxybutynin chloride : a double blind placebo controlled study. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1990;97(June):521‐6. - PubMed
Thuroff 1991 {published data only}
-
- Thuroff JW, Bunke B, Ebner A, Faber P, Geeter P, Hannappel J, et al. Randomized, double‐blind multicenter trial on treatment of frequency, urgency and incontinence related to detrusor hyperactivity: oxybutynin vs. propantheline vs. placebo. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1990;9(4):337‐8. - PubMed
-
- Thuroff JW, Bunke B, Ebner A, Faber P, Geeter P, Hannappel J, et al. Randomized, double‐blind, multicenter trial on treatment of frequency, urgency and incontinence related to detrusor hyperactivity: oxybutynin versus propantheline versus placebo. Journal of Urology 1991;145(April):813‐7. - PubMed
Ulshofer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ulshofer B, Bihr AM, Bodeker RH, Schwantes U, Jahn HP. Randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study on the efficacy and tolerance of trospium chloride in patients with motor urge incontinence. Clinical Drug Investigation 2001;21(8):563‐9.
-
- Ulshofer B, Schwantes U, Bodeker RH, Bihr AM, Jahn HP. Efficacy and tolerance of trospium chloride in patients with motor urge incontinence ‐ results of a randomised double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Proceedings of the International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI), Paris. 2001:5.
VanKerrebroeck 1998 {published data only}
-
- Messelink EJ, Soler JM, Madersbacher H, Thuroff JW, Amarenco G, Kerrebroeck PEV. Urodynamic aspects of the efficacy of tolterodine, a new anti muscarine drug in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia. Proceedings of the International Continence Society 25th Annual Meeting. 1995:95‐6.
-
- Kerrebroeck PEVA, Amarenco G, Thuroff JW, Madersbacher HG, Lock MTWT, Messelink EJ, Soler JM. Dose‐ranging study ot tolterodine in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1998;17:499‐512. - PubMed
VanKerrebroeck 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chancellor M, Freedman S, Mitcheson HD, Antoci J, Primus G, Wein A. Tolterodine, an effective and well tolerated treatment for urge incontinence and other overactive bladder symptoms. Clinical Drug Investigation 2000 Feb;19(2):83‐91.
-
- Garely A, on behalf of the Tolterodine Study Group. Once‐daily tolterodine treatment significantly decreases perception of urgency and urge incontinence episodes in patients with overactive bladder. International Urology Journal 2001;12(Suppl):18.
-
- Kelleher CJ, Pleil AM, Okano GJ, Reese PR. Long‐term health‐related quality of life of patients with overactive bladder receiving tolterodine. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001;20(4):504‐6.
-
- Kelleher CJ, Pleil AM, Okano GJ, Reese PR. Long‐term health‐related quality of patients with overactive bladder receiving Tolterodine. Proceedings of the International Continence Society Annual Meeting, Seoul. 2001:No. 82.
-
- Kelleher CJ, Pleil AM, Reese PR. Health related quality of life of patients with overactive bladder receiving tolterodine once‐daily. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2000;19(4):519‐21.
Walter 1982 {published data only}
-
- Walter S, Hansen J, Hansen L, Maegaard E, Meyhoff HH, Nordling J. Urinary incontinence in old age. A controlled clinical trial of Emepronium Bromide. British Journal of Urology 1982;54:249‐51. - PubMed
Wehnert 1989 {published data only}
-
- Wehnert VJ, Sage S. Comparative study of the effect of Mictonorm (Propiverine hydrochloride) and Spasuret (Flavoxate hydrochloride) on the bladder detrusor muscle [Vergleichende untersuchungen zur wirkung von Mictonorm (Propiverin hydrodhlorid) und Spasuret (Flavoxat hydrochlorid) auf den detrusor vesicae (German)]. Zentralblatt für Urologie und Nephrologie 1989;82:259‐63. - PubMed
Wehnert 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wehnert VJ, Sage S. Treatment of bladder unstability and urge incontinence with Propiverine Hydrochloride (Mictonorm®) and Oxybutynin chloride (Dridase®) ‐ a randomised crossover study [Therapie der blaseninstabilität und urge‐inkontinenz mit Propiverin hydrochlorid (Mictonorm®) und Oxybutinin chlorid (Dridase®) ‐ eine randomisierte cross‐over‐vergleichsstudie (German)]. Aktuelle Urologie 1992;23:7‐11.
Wein 1978 {published data only}
-
- Wein AJ, Hanno PM, Raezer DM, Benson GS. Effect of oxybutynin chloride on bladder spasm following transurethral surgery. Urology 1978;XII(2):184‐6. - PubMed
Zeegers 1987 {published data only}
-
- Zeegers AGM, Kiesswetter H, Kramer AEJL, Jonas U. Conservative therapy of frequency, urgency and urge incontinence: a double‐blind clinical trial of flavoxate hydrochloride, oxybutynin chloride, emepronium bromide and placebo. World Journal of Urology 1987;5:57‐61.
Zinner 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zinner NR, Mattiasson A, Stanton SL. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of extended‐release once‐daily tolterodine treatment for overactive bladder in older versus younger patients. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50(5):799‐807. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zinner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zinner N, Gittelman M, Harris R, Susset J, Kanelos A, Auerbach S, Trospium Study Group. Trospium chloride improves overactive bladder symptoms: a multicenter phase III trial. Journal of Urology 2004;171(6 (Pt 1)):2311‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zorzitto 1989 {published data only}
-
- Zorzitto ML, Holliday PJ, Jewett MAS, Herschorn S, Fernie GR. Oxybutynin chloride for geriatric urinary dysfunction: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Age and Ageing 1989;18:195‐200. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alloussi 1998a {published data only}
-
- Alloussi S, Laval K‐U, Mertins B. Efficacy and tolerability of trospium chloride (spasmo‐lyt) versus placebo in patients with motor urge‐syndrome. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 28th Annual Meeting; 1998 Sept 14‐17; Jerusalem, Israel; 1998 109‐10. [MEDLINE: ]
Andersen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Andersen JR, Lose G, Norgaard M, Stimpel H, Andersen JT. Terodiline, Emepronium bromide or placebo for treatment of female detrusor overactivity? A randomized, double‐blind cross‐over study. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 17th Annual Meeting; 1987 Sept 2‐5; Bristol,UK; 1987 1‐2. [MEDLINE: ]
Appell 1997 {published data only}
-
- Appell RA. Clinical efficacy and safety of tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder: A pooled analysis. Urology 1997;50(Suppl 6A):90‐6. - PubMed
Baert 1995 {published data only}
-
- Baert L, Leuven G, Dijkman B, the Darifenacin study group. [Darifenacin, a novel M3 muscarinic receptor antagonist in detrusor overactivity [Read by title abstract]]. Proceedings of the 25th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society, Sydney, Australia. 1995.
Brocklehurst 1972 {published data only}
-
- Brocklehurst JC, Armitage P, Jouher AJ. Emepronium bromide in urinary incontinence. Age and Ageing 1972;1:152‐7. - PubMed
Burgio 1994 {published data only}
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS, Hardin JM, McDowell BJ, Candib D. Behavior vs drug therapy for urge incontinence in older women (Abstract). Proceedings of the American Urogynecology Society, 15th Annual Scientific Meeting; 1994 Sept 21‐24; Toronto, Ontario. 1994:48 (Abstract 26).
Cardozo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cardozo L, Dixon A. Increased warning time with darifenacin: a new concept in the management of urinary urgency. Journal of Urology 2005;173(4):1214‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chapple 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chapple CR, Madersbacher H, Dreikorn K, Dorschner W, Murtz G. Urodynamics and frequency/volume chart ‐ do they correlate? Treatment analysis of Propiverine in comparison to Oxybutynin and Placebo in urge incontinence (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 31st Annual Meeting; 2001 Sept 18‐21; Seoul, Korea. 2001:Abstract 224. [MEDLINE: ]
Chapple 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chapple CR, Arano P, Bosch JHR, Ridder D, Kramer G, Ridder AM. YM905 appears effective and well tolerated in patients with symptomatic idiopathic detrusor overactivity in a European placebo‐ and tolterodine‐controlled, phase‐II, dose‐finding study (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(4):381‐2. [MEDLINE: ]
Chapple 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chapple C, Rechberger T, Al‐Shukri S, Meffan P, Everaert K, Ridder A. Results of a randomized phase 3 study comparing solifenacin succinate with tolterodine and placebo in patients with symptomatic overactive bladder (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2003;22(5):534‐5. [MEDLINE: ]
Chapple 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chapple C. Fesoterodine a new effective and well‐tolerated antimuscarinic for the treatment of urgency‐frequency syndrome: results of a phase 2 controlled study (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2004;23(5/6):598‐9. [MEDLINE: ]
Chapple 2005a {published data only}
-
- Chapple C, Steers W, Norton P, Millard R, Kralidis G, Glavind K, et al. A pooled analysis of three phase III studies to investigate the efficacy, tolerability and safety of darifenacin, a muscarinic M3 selective receptor antagonist, in the treatment of overactive bladder. British Journal of Urology International 2005;95(7):993‐1001. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coombes 1994 {published data only}
-
- Coombes GM, Millard RJ. A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial of penthienate in the treatment of detrusor instability (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society 24th Annual Meeting; 1994 Aug 30 ‐ Sept 2; Prague, Czech Republic; 1994 104. [MEDLINE: ]
Davila 2001a {published data only}
-
- Davila GW, Daugherty CA, Sanders SW, for The Transdermal Oxybutynin Study Group. A short‐term, multicenter, randomized double‐blind dose titration study of the efficacy and anticholinergic side effects of transdermal compared to immediate release oral oxybutynin treatment of patients with urge urinary incontinence. Journal of Urology 2001;166(July):140‐5. - PubMed
Di Stasi 2001b {published data only}
-
- Stasi SV, Giannantoni A, Navarra P, Capelli G, Storti L, Porena M, Stephen RL. Intravesical oxybutynin: mode of action assessed by passive diffusion and electromotive administration with pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin and n‐desethyl oxybutynin. Journal of Urology 2001;166:2232‐6. - PubMed
Dorschner 2003b {published data only}
-
- Dorschner W, Stolzenburg JU, Griebenow R, Halaska M, Brunjes R, Frank M, et al. [The elderly patient with urge incontinence or urge‐stress incontinence ‐ efficacy and cardiac safety of propiverine]. [German]. Aktuelle Urologie 2003;34(2):102‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gerstenberg 1986 {published data only}
-
- Gerstenberg TC, Klarskov P, Ramirez D, Hald T. Terodiline in the treatment of women with urgency and motor urge incontinence. A clinical and urodynamic double‐blind cross‐over study. British Journal of Urology 1986;58(2):129‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goode 2004 {published data only}
-
- Goode PS. Behavioral and drug therapy for urinary incontinence. Urology 2004;63(Suppl 3A):58‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Griebenow 1994 {published data only}
-
- Griebenow R, Wieners F, Lange Th. Possible induction of cardiac dysrhythmia in elderly patients under therapy with propiverine hydrochloride. Neurourology and Urodynamics. 1994; Vol. 13:430‐2.
Kirschner‐Hermanns {published data only}
-
- Kirschner‐Hermanns R, DuBeau C, Resnick NM. Oxybutynin for incontinence in institutionalized elderly ‐ a re‐evaluation. Proceedings of the International Continence Society 27th Annual Meeting. 1997:149‐50.
Kuipers 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kuipers M, Tran DD, Krauwinkel W, Abila B, Mulder H. Absolute bioavailability of YM905 in healthy male volunteers: A single‐dose, randomized, two‐period crossover study (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug 28‐30; Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:296‐7. [MEDLINE: ]
Larsson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Larsson G, Hallen B, Nilvebrant L. Tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder: analysis of the pooled phase II efficacy and safety data. Urology 1999;53(5):990‐8. - PubMed
Norton 1994 {published data only}
-
- Norton P, Karram M, Wall LL, Rosenzweig B, Benson JT, Fantl JA. Randomized double‐blind trial of terodiline in the treatment of urge incontinence in women. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1994;84(3):386‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ouslander 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ouslander JG, Schelle JF, Uman G, Fingold S, Nigam JG, Tuico E. Does oxybutynin add to the effectiveness of prompted voiding for urinary incontinence among nursing home residents?. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1995;43:610‐7. - PubMed
Robinson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Robinson JM, Brocklehurst JC. Emepronium bromide and flavoxate hydrochloride in the treatment of urinary incontinence associated with detrusor instability in elderly women. British Journal of Urology 1983;55:371‐6. - PubMed
Rosario 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rosario DJ, Smith DJ, Radley SC, Chapple CR. Pharmacodynamics of anticholinergic agents measured by ambulatory urodynamic monitoring: a study of methodology. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1999;18:223‐34. - PubMed
Rudy 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rudy D, Cline K, Goldberg K, Harris R. A multicenter, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of trospium chloride in overactive bladder patients (Abstract). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2004;23(5/6):600‐1. [MEDLINE: ]
Smith 2002 {published data only}
-
- Smith N, Grimes I, Ridge S, Tempel D, Uchida T, Yamanouchi USA. YM905 is effective and safe as treatment of overactive bladder in women and men: results from phase II study (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug 28‐30; Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:138‐9. [MEDLINE: ]
Staskin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Staskin DR, Harnett MD. Effect of trospium chloride on somnolence and sleepiness in patients with overactive bladder. Current Urology Reports 2004;5(6):423‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Takayasu 1990 1 {published data only}
-
- Takayasu H, Ueno A, Tsutida S, Koiso K, Kurita K, Kawabe K, et al. Clinical effects of propiverine hydrochloride in the treatment of urinary frequency and incontinence associated with detrusor overactivity: a double blind, parallel, placebo controlled multicenter study. Igaku No Ayumi (Progress in Medicine) 1990;153:459‐71. [MEDLINE: ]
Tapp 1987 {published data only}
-
- Tapp A, Fall M, Norgaard J, Massey A, Choa R, Carr T, et al. A dose‐titrated, multicentre study of terodiline in the treatment of detrusor instability. Neurourololgy and Urodynamics. 6 1987; Vol. 6, issue 3:254‐5. [MEDLINE: ]
Tapp 1989 {published data only}
-
- Tapp A, Fall M, Norgaard J, Massey A, Choa R, Carr T, Korhonen M, Abrams P. Terodiline: a dose titrated, multicenter study of the treatment of idiopathic detrusor instability in women. Journal of Urology 1989;142(4):1027‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Terodiline 1993 {published data only}
-
- Terodiline in the Elderly American Multicenter Study Group. Effects of terodiline on urinary incontinence among older non‐ institutionalized women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1993;41(9):915‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Viayna 2004 {published data only}
-
- Viayna C, Alvarez D, Lopez R, Sanagustin J, Lagunas C. A randomised, placebo‐controlled, dose‐rising study in healthy males volunteers to evaluate safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single oral doses of SVT‐40776, a novel selective M3 antimuscarinic (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (34th Annual Meeting) and the International UroGynecological Association; 2004 Aug 23‐27;Paris;. 2004:Abstract number 270. [MEDLINE: ]
Wagg 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wagg A, Malone‐Lee J. Pressure‐flow variables in patients treated with tolterodine for detrusor overactivity. BJU International 2003;92(9):969‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wein 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wein AJ, Appell RA. A comparison of the efficacy response profile of tolterodine and oxybutynin. International Urogynaecology Journal. 1999; Vol. 10 (Suppl 1):150.
-
- Wein AJ, Appell RA. A comparison of the efficacy response profile of tolterodine and oxybutynin [Read by title abstract]. Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society; 1999 Aug 23‐26; Denver, Colorado. 1999:252‐3.
Whitehead 1967 {published data only}
-
- Whitehead JA. Urinary incontinence in the aged. Propantheline bromide as an adjunct to treatment. Geriatrics 1967;22(1):154‐8. - PubMed
Williams 1981 {published data only}
-
- Whitehead JA. Urinary incontinence in the aged. Propantheline bromide as an adjunct to treatment. Geriatrics 1967;22(1):154‐8. - PubMed
-
- Williams AJ, Prematalake JKTG, Palmer RL. A trial of emepronium bromide for the treatment of urinary incontinence in the elderly mentally ill. Pharmatherapeutica 1981;2(8):539‐42. - PubMed
Additional references
Abrams 1988
-
- Abrams PH, Blaivas JG, Stanton SL, Andersen JT. Standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1988;7(5):403‐27.
Abrams 2002
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub‐committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(2):167‐78. - PubMed
Alhasso 2006
-
- Alhasso AA, McKinley J, Patrick K, Stewart L. Anticholinergic drugs versus non‐drug active therapies for overactive bladder syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 4. [Art. No.: CD003193. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003193.pub3] - PubMed
Brieger 1996
-
- Brieger GM, Yip SK, Hin LY, Chung TK. The prevalence of urinary dysfunction in Hong Kong Chinese women. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;88(6):1041‐4. - PubMed
Brown 1999
-
- Brown JS, Grady D, Ouslander JG, Herzog AR, Varner RE, Posner SF. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and associated risk factors in postmenopausal women. Heart & Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999;94(1):66‐70. - PubMed
Chapple 2005b
-
- Chapple C, Khullar V, Gabriel Z, Dooley JA. The effects of antimuscarinic treatments in overactive bladder: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. European Urology 2005;48(1):5‐26. - PubMed
Choo 2001
-
- Choo M‐S, Lee YS, Kim HY, Lee JB, Kwon DD, Lee T, et al. The prevalence of overactive bladder in Korea. Proceedings of the International Continence Society. Seoul, 2001.
de Groat 1997
-
- Groat WC. A neurologic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 1997;50(Suppl 6A):36‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, editors. Analysing and presenting results. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [update May 2005]; Section 8. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2005. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005.
Dorschner 2003a
-
- Dorschner W, Stolzenburg JU, Griebenow R, Halaska M, Brunjes R, Frank M, et al. [The elderly patient with urge incontinence or urge‐stress incontinence ‐ efficacy and cardiac safety of propiverine]. [German]. Aktuelle Urologie 2003;34(2):102‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DuBeau 2000
-
- DuBeau CE, Miller KL, Bergmann M, Resnick NM. Urge incontinence outcomes in RCTs depend on assumed and not actual drug assignment [Abstract]. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2000;19(4):492.
Dublin 2004
-
- Dublin N, Alhasso AA, Stewart L. Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 2. [Art. No.: CD003190. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003190.pub2] - PubMed
Hay‐Smith 2005
-
- Hay‐Smith J, Herbison P, Ellis G, Morris A. Which anticholinergic drug for overactive bladder symptoms in adults?. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3. [Art. No.: CD005429. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005429] - PubMed
Hennessey 1999
-
- Hennessey A, Robertson NP, Swingler R, Compston DA. Urinary, faecal and sexual dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology 1999;246(11):1027‐32. - PubMed
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2005. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005.
Jackson 1997
-
- Jackson S. The patient with an overactive bladder ‐ symptoms and quality of life issues. Urology 1997;50(Suppl. 6A):18‐22. - PubMed
Kobelt 1997
-
- Kobelt G. Economic considerations and outcome measurement in urge incontinence. Urology 1997;50(6A suppl):100‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lawrence 2000
-
- Lawrence M, Guay DR, Benson SR, Anderson MJ. Immediate‐release oxybutynin versus tolterodine in detrusor overactivity: a population analysis. Pharmacotherapy 2000;20(4):470‐5. - PubMed
Milsom 2001
-
- Milsom I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Roberts RG, Thuroff J, Wein AJ. How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population‐based prevalence study. BJU International 2001;87(9):760‐6. - PubMed
Moller 2000
-
- Moller LA, Lose G, Jorgensen T. The prevalence and bothersomeness of lower urinary tract symptoms in women 40‐60 years of age. Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2000;79(4):298‐305. - PubMed
Moothy 2001
-
- Moothy P, Lapitan MC, Lim PHC. Prevalence of overactive bladder in Asian males: an epidemiologic survey. Proceedings of the International Continence Society. Seoul, 2001.
Ouslander 1982
-
- Ouslander JG, Kane RL, Abrass IB. Urinary incontinence in elderly nursing home patients. JAMA 1982;248(10):1194‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ouslander 1986
-
- Ouslander JG, Hepps K, Raz S, Su HL. Genitourinary dysfunction in a geriatric outpatient population. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1986;34(7):507‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pleil 2005
-
- Pleil AM, Coyne KS, Reese PR, Jumadilova Z. The Validation of Patient‐Rated Global Assessments of Treatment Benefit, Satisfaction, and Willingness to Continue‐The BSW. Value in Health 2005;8:S25‐34. - PubMed
Stewart 2001
-
- Stewart WF, Corey R, Herzog AR, Wein A, Norton PA, Payne C, et al. Prevalence of overactive bladder in women: results from the Noble Program. International Urogynecology Journal. 2001; Vol. 12 (3):66.
Ueda 2000
-
- Ueda T, Tamaki M, Kageyama S, Yoshimura N, Yoshida O. Urinary incontinence among community‐dwelling people aged 40 years or older in Japan: prevalence, risk factors, knowledge and self‐perception. International Journal of Urology 2000;7(3):95‐103. - PubMed
van Kerrebroeck 2001
-
- Kerrebroeck PHEV, for the Tolterodine study group. Long‐term tolerability and efficacy of once‐daily (OD) tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB). International Urogynecology Journal. 2001; Vol. 12 (Suppl 3):549.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

